Three NanoPhoton Lectures on 18 February
On 18 February we will have three NanoPhoton Lectures in 421/072 at 15:00-16:30. They are:
'Light Meets Spin: Spectroscopic Insights into Low-dimensional Materials' by Professor Vladimir Dyakonov from Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg, Germany.
Abstract:
In this talk, I will present examples that highlight the capabilities of optically detected magnetic resonance in revealing the nature and functional role of spin excitations in quantum sensing and optoelectronic applications. This talk is divided into two parts. The first part focuses on two-dimensional material hBN while the second part addresses spin-spin interactions in molecular light-emitting diodes.
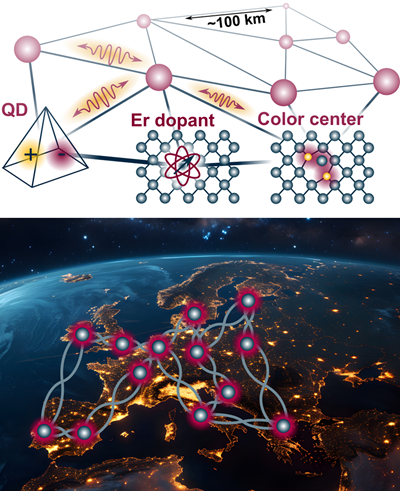
'Satellite-based quantum communication networks' by Professor Dr. Tobias Vogl from the Technical University of Munich, Germany.
Abstract:
Near-future optical quantum technologies promise advances in quantum computing, communication, and nanoscale sensing, enabled by reliable single-photon sources. Solid-state color centers are widely used for this purpose, with defects in two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) offering chemical and thermal robustness and bright room-temperature emission. We report recent progress in engineering these emitters and coupling them to resonant optical and integrated photonic platforms, combined with on-chip room-temperature silicon single-photon detectors. This realizes a programmable quantum logic circuit for state preparation, manipulation, and detection, demonstrated in the QUICK³ space mission as a prototype for future satellite-based quantum communication and the quantum internet.
'He-ion beam induced quantum emitters in MoS2' by Dr. Christoph Kastl from the Technical University of Munich, Germany.
Abstract:
Focused He-ion beam exposure can create functional defects in 2D materials, such as single photon emitters in MoS2 with a spatial resolution well below 10 nm. I will discuss how to quantify and disentangle different contributions to the line shape of single photon emitters in helium-ion treated monolayer MoS2, including homogeneous broadening, thermal broadening, and acoustic phonon sidebands. I will compare a simple independent boson model to temperature dependent emission spectra of the single photon emitters. Lastly, I will briefly comment on current microscopic pictures for the atomistic origin of the single photon emission in MoS2.
New colleagues in NanoPhoton
A warm welcome to postdoc Xujing Liu and PhD student Enrico Vallar who joined us recently.
Xujing's research will focus on resource-efficient, programmable photonic integrated circuits. By leveraging ultrafast electro-optic control in cavity-based architectures, it aims to develop temporal-mode photonic processors with reduced footprint and control complexity.
Enrico is investigating the cooperative dynamics between multiple quantum emitters and their applications. He is working on their enhancement through the design and fabrication of effective near-zero-index metamaterials.

New paper in ACS Photonics
Our paper 'Orders of Magnitude Reduction in Photonic Mode Volume by Nanosculpting' was published in ACS Photonics.
Using advanced photonic inverse‑design techniques, allowing fully freeform 3D structures, we uncover seemingly optimal axisymmetric geometries. These findings allow us to explore, map and push the limits of light–matter interaction at the nanoscale. Our results show how precise control of material response and geometry in all three dimensions can unlock photonic performance that goes beyond current state‑of‑the‑art. While today's nanofabrication cannot yet realize these structures, the study highlights the immense potential of fully 3D photonic architectures once fabrication capabilities catch up.

NanoPhoton on the cover of Science Advances
Our latest paper, 'A nanolaser with extreme dielectric confinement', has just been published in Science Advances – and it even made the cover!
We report the first experimental demonstration of a nanolaser operating at room temperature under continuous-wave pumping, with light confined to an optical mode volume below the diffraction limit. The laser is based on the topology-optimized design first presented in Applied Physics Letters by Wang, Christiansen, Yu, Mørk, and Sigmund (APL 114, 241101, 2018), which laid the foundation for the NanoPhoton research program. Achieving a high-quality nanolaser required new theoretical modeling and the development of advanced fabrication techniques, in particular a novel passivation approach that enables nanocavity definition without compromising the active material.

Alisha Nanwani defended her PhD thesis
On 18 December, Alisha Nanwani, successfully defended her thesis entitled ‘Selective Epitaxy of III-V/Si Nanostructures for Extreme Dielectric Confinement’.
A special thank you to the assessment committee, chaired by Professor Nini Pryds, DTU Energy, and the external examiners Professor Jonas Johansson, Lund University, Sweden and Senior Engineer Heinz Schmid, IBM, Switzerland. Also, thank you to the principal supervisor, Senior Researcher Elizaveta Semenova, co-supervisors Professor Kresten Yvind and Dr. Paweł Holewa and the master of the ceremony, Senior Researcher Mikkel Heuck.

NanoPhoton Lecture by Anton Zasedatelev
Anton Zasedatelev, Aalto University, Finland, visited NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics and gave a talk on 'Quantum optomechanics with polaritons'.He presented exciting experimental and theoretical results from his group on optomechanical interactions in polaritonic systems, including Bose–Einstein condensation, prospects for achieving phonon Bose–Einstein condensation, and the possibility of generating entanglement in polariton systems at room temperature via optomechanical interactions.

NanoPhoton tutorials by Dr. Moritz Cygorek
Moritz Cygorek from the Technical University of Dortmund, Germany, spent the month of November with NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics. During his stay, he gave a series of tutorials on ‘Open quantum system theory for solid–state quantum emitters’ for which attending students could earn ECTS points.
The tutorials covered modern techniques to predict the dynamics of open quantum systems when the coupling to their surrounding environment is not weak. In this rather common scenario, the quantum dynamical evolution of the environment leads to non-Markovian memory effects on the quantum system. Central to the course was the introduction of methods beyond Markovian master equations, the phenomena resulting from non-Markovian system-environment interactions, and their impact on applications in quantum technologies. A particular focus is put on the numerically exact process tensor framework. These concepts and techniques are applied to the example of solid-state quantum emitters embedded into photonic structures, where non-Markovian phonon effects have a strong impact on state preparation and non-classical light generation.

New paper out in Nano Letters
In a paper entitled 'Nanoelectromechanical Spectral Control of Silicon Bowtie Nanocavities for Quantum Light Sources' published in Nano Letters we demonstrated subwavelength light confinement and reversible spectral control with ultralow power consumption using electromechanically tunable silicon bowtie nanocavities.
This innovative cavity design offers:
- Tuning range across 11 nm at telecom wavelengths
- Cryocompatibility
- High Purcell factors
- Efficient waveguide integration
Together, these advances mark an important step toward scalable cavity quantum electrodynamics (cQED) and the future of silicon-based quantum photonics

Paper in Physical Review Research
In the paper 'Strong coupling between a dielectric nanocavity and a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide' we demonstrate strong coupling between an extreme dielectric confinement cavity and a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide. In the strong coupling regime, the light-matter interaction strength overcomes the averaged losses of the system (in our case, even by a factor of ~2).
We measure avoided crossing with two experimental methods (PL and reflection measurements). The experimental values for the light-matter interaction strength are in excellent agreement with simulations obtained in the exciton reaction coordinate formalism, based on quasinormal modes and FEM simulations. The combination of tight lateral confinement of light, the large oscillator strength of the excitons and the small losses associated with dielectric cavities holds great promises for nonlinear effects on the single-photon level.

Talk for the 35 finalists of the national Physics Olympics
Valdemar Bille-Lauridsen gave a popular science talk at the new Niels Bohr Building for the 35 finalists of the national Physics Olympiad.
The talk entitled “Nanophotonics, Communication and Quantum Technology” focused on disseminating the importance of nanophotonics in both current and future communication technologies, and how it may be employed in quantum technologies.The presentation covered fundamental principles of nanolasers and quantum dots, as well as insights from Valdemar’s current research, where the fundamental limits of light confinement are explored and ultra-efficient nanolasers are developed.
This is an example of an outreach initiative we engage in.

Paper out in Laser & Photonoics Reviews
Our paper, 'Enhancement and Speed-Up of Carrier Dynamics in a Dielectric Nanocavity with Deep Sub-Wavelength Confinement', demonstrates how extreme light confinement in a bowtie cavity can significantly accelerate carrier diffusion and boost switching contrast. This work highlights NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics’s core approach: combining topology optimization, nanofabrication, experimental characterization, and fundamental theory to unlock new possibilities when light is confined to deep sub-wavelength scales. The findings pave the way for low-power nanophotonic devices such as efficient and fast switches and modulators.

Welcoming new colleagues to NanoPhoton
We are welcoming Emil Rødbro and Ali Nawaz Babar to NanoPhoton.
Emil works with light matter interaction, extreme confinement of light and spin-physics in relation to erbium in silicon, as a platform for quantum information processing and single-photon emitters.
Ali completed his PhD in 2024 with NanoPhoton, where he worked on the fabrication and characterization of silicon photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement. He specializes in nanofabrication, integrated photonics, and nanoelectromechanical systems, and is deeply passionate about driving the development of next-generation photonic technologies.

NanoPhoton goes to NANOP 2025 conference
Amedeo Carbone, Benjamin Gøtzsche, and Simon Klinck Borregaard, attended the NANOP 2025 conference in Paris, where they attended inspiring talks on functional nanophotonics from experts in the field. Amedeo gave a talk on quantifying the creation of negatively charged boron vacancies in He-ion-irradiated hexagonal boron nitride, Benjamin gave a talk on self-induced back-action forces in electromagnetic resonators, and Simon presented his poster on experimental demonstration of a high quality-factor bound state in the continuum in a subwavelength nanocylinder.

Congratulations to dr. Kristian Seegert
Kristian Seegert, successfully defended his thesis entitled ‘Theory and experimental characterization of nanostructured lasers’ on 17 November.
A special thank you to the assessment committee, chaired by associate professor Francesco Da Ros, DTU Electro, and the external examiners professor Jan Wiersig, Otto-von- Guericke-Universität Magdeburg, Germany and associate professor Nick Volet, Aarhus University, Denmark. Also, thank you to the principal supervisor, professor Jesper Mørk, co-supervisors senior researcher Yi Yu and senior researcher Mikkel Heuck and the master of the ceremony, professor Martijn Wubs.

New paper on the street
We have a new paper published in Laser & Photonics Reviews entitled 'Carrier Transport in Electrically-Driven Photonic Crystal Membrane Lasers'.
To address the ever-growing energy demand of data centres, optical interconnects are emerging as a faster and more efficient alternative to conventional electrical links for on-chip and chip-to-chip communication. Energy-efficient and compact light sources are key to this transition. In particular, lateral current injection photonic crystal nanolasers have seen tremendous advancements in achieving ultra-low threshold currents. However, their performance remains limited by carrier leakage and low injection efficiencies.
This recent work aims to better understand these limitations. To do this, we developed a two-dimensional carrier transport model that includes gain and stimulated recombination processes. Our model captures the presence of unconventional leakage paths and enhanced spontaneous recombination at the p-doped InP interface, which is consistent with experimental observations. Through a detailed analysis of the electronic band structure, we identify the offset of the p-doped region as a crucial design parameter for improving the injection efficiency, offering valuable insights for optimising electrically driven nanolasers

Meeting with the DNRF
On 4 November, we had the pleasure of welcoming Dorthe Juul Jensen, Niels Mejlgaard, and Morten Andreasen from the Danish National Research Foundation for our annual follow-up visit. As always, the meeting was both inspiring and thought-provoking. We discussed the latest developments in NanoPhoton’s research, celebrated successes, reflected on challenges, and shared insights into the daily life at the centre. A highlight of this year’s dialogue was the DNRF’s question: “What are the conditions for risk-taking in the context of Centers of Excellence?” This sparked a rich conversation about how bold ideas and calculated risks shape groundbreaking research.
A big thank you to the DNRF for your keen interest in our field and your continued support—it truly makes a difference!

Paper in Nano Letters
Our latest publication '3D Imaging of Optical Modes in Dielectric Photonic Nanocavities with Sub-wavelength Field Confinement', was published in Nano Letters.
This study presents the direct visualization of optical modes in a topology-optimized silicon bowtie nanocavity using multi-orientation electron energy-loss spectroscopy. Through tomographic reconstruction, the three-dimensional structure of several polarised optical modes is revealed, showing excellent agreement with simulations. The targeted mode near the bowtie bridge is found to be tightly confined, confirming a deep sub-wavelength mode volume. These findings establish electron beam spectroscopy as a powerful technique for mapping three-dimensional field confinement in dielectric photonic cavities, opening new opportunities for next-generation photonic and quantum technologies.
Villum Synergy Grant toSanshui Xiao
Associate professor Sanshui Xiao and professor Zheng-Hua Tan (AAU, Aalborg University) have been awarded a Villum Synergy Grant to develop next-generation quantum light sources in a groundbreaking interdisciplinary research project entitled ‘Leveraging Machine Learning for Developing On-Chip Quantum Sources with 2D Materials Integration’. It aims to transform quantum technologies by integrating machine learning (ML) with advanced 2D photonic materials.
The synergy between DTU’s expertise in nanophotonics and AAU’s expertise in machine learning will drive innovations across three key work packages:
WP1: Rapid identification and fabrication of high-quality 2D superlattices using ML-enhanced imaging techniques.
WP2: ML-assisted quantum measurement to distinguish single-photon sources.
WP3: Optimization of photonic nanostructures using deep learning methods to achieve high efficiency.
“This project represents a bold step toward scalable, efficient quantum devices,” said Sanshui Xiao. “By combining machine learning with 2D materials, we aim to unlock new possibilities for quantum photonics.” The research is expected to have a significant impact on the development of integrated quantum technologies, making them more accessible and practical for real-world applications.

Congratulations to Beñat
Beñat Martinez de Aguirre Jokisch successfully defended his thesis entitled ‘Multiphysics topology optimization in nanophotonics’ on Friday, 24 October.
During his PhD, Beñat studied the development of topology optimization methods for thermo-optics [1], electro-optics [2], opto-mechanics, including optical trapping [3] and engineering of optical forces [4]. A special thank you to the assessment committee, chaired by associate professor Thomas Christensen, DTU Electro, and the external examiners, associate professor Xiaojia Shelly Zhang, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA, and associate professor Richard Norte, Delft University of Technology, Netherlands. Also, thank you to principal supervisor professor Ole Sigmund, co-supervisors professor Jesper Mørk, and associate professor Rasmus E. Christiansen, and the master of the ceremony associate professor Niels Aage.

A successful NanoPhoton workshop
We have just returned from our annual workshop, and what a good experience it was! From discussions on the past, present, and future of NanoPhoton, to a lively poster session by our PhD students and postdocs – the atmosphere was buzzing with curiosity and collaboration.
In preparation for our upcoming annual meeting with the DNRF, we also discussed the theme of risk-taking within the DNRF Centers of Excellence - a topic that generated considerable interest and valuable suggestions. One key challenge identified was the short duration of Danish PhD projects, which, at only three years, poses a significant barrier to pursuing high-risk research.

DTU Electro and NanoPhotonhosted the European Semiconductor and Laser Workshop 2025
The European Semiconductor Laser Workshop has taken place every year since 1978. This year we gathered at the Technical Unviversity of Denmark to share and discuss the latest results within semiconductor laser research, ranging from fundamental laser physics to new materials and improved performance of lasers.
We were treated to brilliant keynote talks by Åsa Haglundfrom Chalmers (SE) and Meir Orenstein from Technion (IL), who sparked lively discussions and new ideas.
The workshop also featured inspiring invited talks by Fabrice Raineri(Université Côte d’Azur, FR), Maciej Pieczarka(Wroclaw University, PL), Francesco Cappelli (CNR-INO, IT), and Claire Besançon (III-V Lab, FR).

NanoPhoton Lecture by Richard Norte on 23 October
Dr. Richard Norte, Delft University of Technology, the Netherlands, will give a lecture on 'Extreme-Aspect-Ratio Nanostructures: From Quantum Oscillators to Interstellar Lightsails' on 23 October at 15:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
For the past half century, Moore’s Law has steered nanotechnology toward miniaturizing components in all three dimensions. As we reach its limits, our lab explores a new class of nanotechnology whose components span centimeters in x and y while remaining nanometers thick in z. These extreme-aspect-ratio nanostructures display properties not found in conventional nanosystems and open new regimes for precision measurement and quantum science.
I will present nanomechanical resonators that combine centimeter-scale footprints with nanometer thickness, achieving room-temperature quality factors approaching 10 billion at kilohertz frequencies, comparable to state-of-the-art cryogenic systems. Their designs are optimized using machine learning algorithms that efficiently explore large, bio-inspired design spaces while remaining grounded in the realities of fabrication. Beyond quantum oscillators, we employ the same approaches to create nanophotonic lightsails for Breakthrough Starshot, some of the highest-aspect-ratio nanophotonic components ever produced. Together, these advances open pathways to room-temperature quantum computing, ultrasensitive force sensing, and entirely new measurement concepts not achievable at smaller length scales.
-0-
Norte gave an inspiring talk in an area that mixes the physics of nano-photonics and mechanics: engineering extreme aspect ratio structures to realise ultra-thin opto-mechanical membranes. It was fascinating to witness this work on experiments, modelling and design of one-gram nano-satellites intended for speedy exploration of our solar system.

Exciting news from NanoPhoton!
We are thrilled to announce that NanoPhoton has been invited to enter contract negotiations for an additional four years of funding from the DNRF (Danish National Research Foundation).
During the first phase of NanoPhoton, we demonstrated a new class of semiconductor nanocavities capable of focusing light into hotspots far smaller than the wavelength of light.
In the upcoming second phase, our goal is to integrate emitters into these nanocavities—a step that will enable strong light–matter interactions with transformative potential for nanolasers, optoelectronics, and quantum technologies.
We are deeply grateful to the DNRF for their continued support and trust in our research. Here’s to pushing the boundaries of nanophotonics even further.

Expanding computational capabilities with Gefion
Matias Bundgaard-Nielsen and Mikkel Heuck have just been awarded 24,000 GPU-hours on Denmark’s new Gefion supercomputer, funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation and operated by the Danish Centre for AI Innovation (DCAI).
With access to state-of-the-art GPU infrastructure, Mikkel and Matias will accelerate their study of large-scale quantum photonic neural networks. Using advanced computational techniques and optimal control theory, the project will investigate losses and error mitigation in photonic networks composed of dynamically controlled cavities.
We are excited to expand our computational capabilities, and best of luck to Mikkel and Matias in bending some photons (and GPUs) to their will!

PhD defence by Frederik Schröder
Frederik Schröder, successfully defended his thesis on ‘Light-Matter Interactions in Dielectric Nanocavities and 2D Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides’.
A special thank you to the assessment committee, chaired by associate professor Søren Raza, DTU Physics, and the external examiners Professor Ursula Wurstbauer, University of Münster, Germany, and Associate Professor Marcin Syperek, Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Poland.
Also, thank you to principal supervisor associate professor Nicolas Stenger, co-supervisors professor Martijn Wubs, senior researcher Philip Kristensen and professor Jesper Mørk, and the master of the ceremony senior researcher Mikkel Heuck.

Congratulations to the winner of the AEG Juniorprisen 2025
Babak Vosoughi Lahijani wins the AEG Juniorprisen 2025 for his research in photonic circuits, nanoelectromechanical physics, and nanocavities.
Over the past years, Babak has delivered a series of outstanding scientific results, including publications in the world’s top journals such as Nature, Nature Communications, and Nature Photonics and several patents in the field of photonic circuits. His scientific versatility is truly remarkable for a young researcher, and he consistently delivers at the highest level.

NanoPhoton at EOSAM 2025 in Delft
Elizaveta Semenova attended the 13th European Optical Society Annual Meeting, EOSAM 2025, in Delft, the Netherlands.
EOSAM is one of Europe’s premier photonics conferences covering all aspects of optics and photonics through a broad range of topical sessions from quantum and nonlinear optics to nanophotonics, optical materials, biophotonics, fibre technologies, and more.
The event brings together researchers, industry leaders, students, and innovators from over 30 countries.
Elizaveta gave an invited talk entitled 'Engineering Quantum Dot Quantum Light Sources for Telecom: Challenges and Future Directions'.

New NanoPhoton member
Avishek Sarbajna joined us in July as a postdoc. He will investigate light-matter interaction in active EDC, buried heterostructures and photonic crystal cavities.

External stay at the EPFL in Lausanne
Benjamin Gøtzsche spent the spring in Lausanne, Switzerland, at École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL). During his stay, he was a part of the Nanophotonics and Metrology Laboratory led by Olivier J.F. Martin, working on optical forces associated with anisotropic particles.

Press release from the IEEE Photonics Society highlights NanoPhoton research on nanolasers
Led by Prof. Jesper Mørk of the DTU - Technical University of Denmark, the research demonstrates how miniaturized laser cavities can operate at ultra‑low powers, challenging traditional laser physics and making compact, energy‑efficient light sources a reality. Key advances include:
• Photonic crystal nanolasers achieving room‑temperature operation at record‑low threshold currents (as low as 730 nA)
• Deep subwavelength cavities breaking optical confinement limits
• Fano nanolasers offering improved spectral characteristics for high‑speed optical systems.
Read the full paper.

Award for best student talk at SCOM
Frederik Schröder gave a talk at the SCOM conference in Odense on 'Strong coupling between a dielectric nanocavity and a monolayer transition metal dichalcogenide' and won the best student talk award. The conference brings together established world experts and emerging research leaders from fields such as organic chemistry, condensed-matter physics, nanophotonics, quantum optics, materials science, and engineering. The conference topics cover all aspects of strong light—matter coupling

Talks at CLEO Europe 2025 in Munich
We have members participating and giving talks at CLEO Europe 2025 this week.
Valdemar Bille-Lauridsen: 'Experimental characterisation of nanoscale buried heterostructure quantum wells', session CK-11.5, Thursday 17:00, ICM Room 14b.
Gaoneng Dong: 'Ultrafast dynamics in semiconductor nanocavities with deep sub-wavelength confinement of light', session CD-13.3, Friday 14:30, ICM Room 13a.
Mathias Marchal: 'Carrier Transport in Electrically-Driven Photonic Crystal Membrane Lasers', session CK-14.3, Friday 14:30, Room 14b.
Matias Bundgaard-Nielsen:' Quantum noise in nanolasers: A new approach', session CB-6.6, Friday 15:15, ICM Room 4b.

NanoPhoton congratulates Prof. Sergey Bozhevolnyi on his 70th birthday
It was a privilege for NanoPhoton members — Andrei Laurynenka, Nicolas Stenger, and Elizaveta Semenova— to attend the 'International Workshop on Emerging Trends in Optics', organised in honour of this milestone, and present their work as invited speakers.
The gathering brought together colleagues and collaborators from across the field to celebrate Prof. Sergey Bozhevolnyi's outstanding contributions to photonics and to engage in inspiring scientific discussions.

Article part of special issue 'Quantum Light: Creation, Integration, and Applications'
Our paper 'Solid-state single-photon sources operating in the telecom wavelength range' was published in Nanophotonics as part of the special issue 'Quantum Light: Creation, Integration, and Applications.
The paper discusses advances in synthesis, integration into photonic devices, and quantum technology applications, while also outlining performance bottlenecks and proposing strategies to push the field toward scalable solutions.
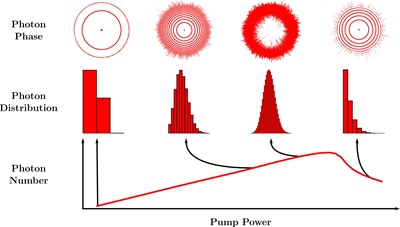
Paper in Physical Review Letters
In our paper 'Simple yet Accurate Stochastic Approach to the Quantum Phase Noise of Nanolasers' accepted in Physical Review Letters, we introduce a simple stochastic algorithm capable of accurately capturing quantum noise in nanolasers. The key to this approach is explicitly modeling the quantum phase of photons, clearly distinguishing spontaneous emission—randomly emitted photons—from stimulated emission, where photons are emitted in sync with an incoming triggering photon.
Our approach naturally connects the microscopic regime (tiny lasers with few emitters, fully quantum) to the macroscopic regime (large-scale lasers, classical description). This bridges an important gap in laser physics and provides practical tools for designing improved nanolasers—important for next-generation quantum technologies and ultra-low-power photonics.
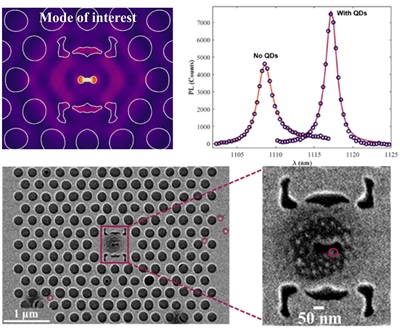
Paper published in Optics and Laser Technology🎉
In the paper ‘Fabrication and characterization of shape- and topology-optimized optical cavities with deep sub-wavelength confinement for interfacing with colloidal quantum dots’, we propose a combined shape- and topology-optimization strategy to design manufacturable two-dimensional photonic crystal-based optical photonic crystal slot nanocavities that confine light to length scales well below the resonance wavelength in the air region with the aim of enhancing light-matter interaction for interfacing with colloidal quantum dots💡
We successfully fabricated the optimised designs and experimentally characterised the resulting structures with and without spin-coated colloidal quantum dots. The results corroborate the potential of the fabrication process for ensuring high yield and reliable performance as well as the viability of the material platform for exploring light-matter interaction with colloidal quantum dots.
New publication editor's suggestion in Phys. Rev. Materials
The paper 'Quantifying the creation of negatively charged boron vacancies in He-ion irradiated hexagonal boron nitride' was published in Phys. Rev. Materials.
Hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) is emerging as a fascinating host for quantum defects—luminescent "colour centres" that could power future technologies in quantum sensing and spin-based devices, even at room temperature.
In this work, we used a focused beam of helium ions to create boron vacancies (VB) in a controlled way. By combining optical magnetic resonance measurements, calculations based on a microscopic charge model, and molecular dynamics simulations, we were able to quantify the efficiency of defect creation - down to reporting that only ~0.2% of all vacancies become the optically active, negatively charged species.
This study offers new tools to engineer quantum defects in 2D materials with precision - an essential step toward scalable quantum technologies.

Anastasiia Vladimirova defended her PhD thesis
Anastasiia successfully defended her thesis on 'Theory of carrier dynamics in silicon hot-electron light sources' on 28 May.
The assessment committee was chaired by professor Jakob Schiøtz, DTU Physics, and the external examiners were dr. Jelena Sjakste, Ecole Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France, and professor N. Asger Mortensen, University of Southern Denmark. Senior researcher Philip T. Kristensen was the master of the ceremony. Professor Søren Stobbe was supervisor and professor Jesper Mørk co-supervisor.

Paper published in Nanophotonics
'Confocal polarization tomography of dielectric nanocavities' was just published in Nanophotonics.
The problem:
Reflection measurements of dielectric nanocavities often exhibit a large background, complicating the analysis and interpretation of measurements.
Our approach:
We record reflection spectra in a confocal geometry. By varying the polarization projection of the input and output fields, we were able to suppress the background completely.
Findings:
Our approach revealed that there is another mode in the cavity that hitherto went unnoticed. Combining the far-field measurements with FEM-simulations and near-field measurements with a sSNOM in a holistic approach, we were able to identify the modes of the system. The general method could in the future be applied to other types of optical cavities.
Elizaveta Semenova invited speaker at OPIC 2025, Yokohama, Japan
Elizaveta Semenova participated as an invited speaker at the International Conference on Nano-photonics, Nano-optoelectronics and Quantum Technology, held as part of the OPTICS & PHOTONICS International Congress 2025 (OPIC’25) in Yokohama, Japan.
The title of her talk was 'Quantum Dot-Based Quantum Light Sources for Telecom Applications: Challenges and Opportunities'. In her talk, Elizaveta presented recent advances in quantum dot–based single-photon sources operating in the telecom C-band, highlighting aspects of epitaxial growth, deterministic nanofabrication, and the strategies toward realising scalable integrated quantum photonics. She outlined key directions for achieving high-performance, on-chip quantum light sources essential for future quantum technologies.

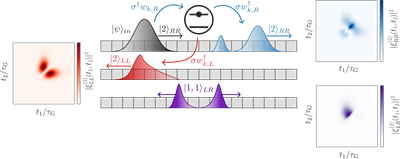
We have developed WaveguideQED.jl
What does a photon look like? If it is a two-photon pulse that has just interacted with a quantum emitter, it might look like a bird.
To answer the question, we have developed WaveguideQED.jl, an open-source package for efficiently simulating the quantum state of propagating photons. We describe the state of photons using many small time-bins, with each bin representing the probability of detecting the photon at that point in time.
In the figure, we show how a photon pulse consisting of two photons scatters off a quantum emitter. The result, which can be calculated using the package, is a complex combination of reflected and transmitted two-photon states, where one can be said to resemble a bird.
For more information about the framework, follow the GitHub link. If you want to know why the "body" of the bird is made out of stimulated emission, check out the paper on the framework, which goes over several usage examples of WaveguideQED.jl.
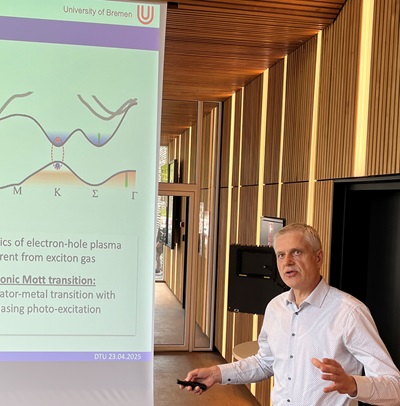
NanoPhoton Lecture by Frank Jahnke on 23 April
Professor Frank Jahnke, University of Bremen, Germany, will give a lecture on 'Many-body effects of excited carriers in atomically thin TMDC semiconductors' on 23 April at 15:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
Atomically thin layers of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs) are structures similar to graphene with an optical bandgap in the visible spectral region and promising optical properties for applications in optoelectronic devices. We study many many-body effects of photoexcited carriers and their ultrafast dynamics. For low and intermediate excited carrier densities, excitons are present even at room temperature with large binding energies due to the two two-dimensional nature of the system and reduced dielectric screening of the Coulomb interaction. In this regime, we study Auger Auger-like exciton exciton-exciton annihilation, which is often considered to be among the most important fundamental constraints on quantum yield in devices based on excitons in two two-dimensional materials [1]. Vertically stacked van der Waals heterobilayers with type type-II band alignment host interlayer excitons (ILX) with drastically increased lifetimes in comparison to excitons within a single layer. We demonstrate that a density density-dependent pronounced blue shift of the ILX due to the repulsive dipole dipole-dipole interaction is almost perfectly compensated by quantum quantum-mechanical exciton exciton-exciton interaction effects [2]. The underlying physics shows that excitons at intermediate densities can no longer be considered as bosons due to interaction effects of their fermionic constituents. For large excited carrier densities above the excitonic Mott transition, giant band band-gap renormalization and optical gain are obtained [3].
[1] A. Steinhoff, F. Jahnke, M. Florian, Microscopic theory of exciton exciton-exciton annihilation in two two-dimensional semiconductors, Physical Review B 104, 155416 (2021).
[2] A. Steinhoff, E. Wietek, M. Florian, T. Schulz, T. Taniguchi, K. Watanabe, S. Zhao, A. Högele, F. Jahnke, and A.Chernikov, Exciton Exciton-exciton interactions in van der Waals heterobilayers, Phys. Rev. X 14, 031025 (2024).
[3] D. Erben, A. Steinhoff, M. Lorke, and F. Jahnke, Optical nonlinearities in the excited carrier density of cally thin transition metal dichalcogenides, Phys. Rev. B 106, 045409 (2022).
---
In his talk, Professor Jahnke shared exciting new results on the fundamental theory of carrier-carrier interactions in TMDC semiconductors. Even at intermediate densities, excitons can not be considered as bosons due to the interaction of the Fermionic constituents. This is shown to have important qualitative and quantitative consequences for a number of effects, like the density-dependence of the interlayer exciton resonance and Auger scattering.
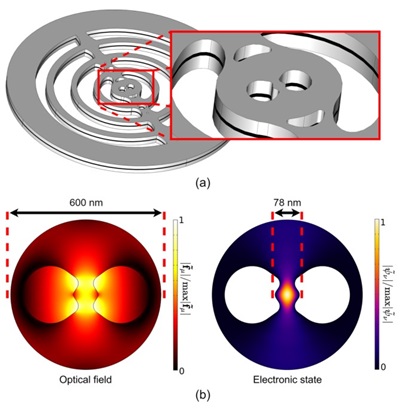
Paper published in Physical Review A
In the paper ‘Waveguide and cavity quantum electrodynamics with topological bowtie modes’ our researchers could combine photonic topological waveguides with nanoscale light confinement for the first time.
We designed and theoretically investigated a photonic waveguide with topological protection to enhance the emissivity of quantum emitters. The giant enhancement has been reached by employing a concept of extreme dielectric confinement.
Paper in Nanophotonics
In a paper entitled 'All-optical switch exploiting Fano resonance and subwavelength light confinement' published in Nanophotonics, we show how a Fano resonance can be combined with a nanocavity featuring sub-wavelength confinement of light to improve the properties of all-optical switches. Bowtie cavity designs have been fabricated, characterized and demonstrated in a wavelength-conversion experiment.

Andrei Lavrinenko recognised by the American Physical Society
Congratulations to Andrei who has been recognized as “Outstanding Referee” by the American Physical Society, which publishes journals from the Physical Review family.
The highly selective Outstanding Referee programme annually recognizes a small percentage of the roughly 50,000 referees who have been asked to review one or more papers in the last twelve months.

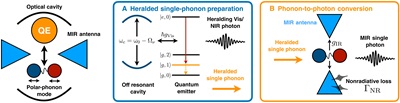
Paper in Science Advances
The paper 'On-demand heralded MIR single-photon source using a cascaded quantum system' proposes a new method to efficiently produce single photons in the mid-infrared (MIR) range. Single photons are crucial for light-based quantum technologies, particularly in quantum metrology and precision spectroscopy, where they enhance measurement accuracy.
Most current single photon sources (SPE) operate in the near-infrared and visible ranges, with low efficiencies in the MIR and terahertz ranges. Developing MIR SPEs could enable non-damaging studies of biological systems, detecting pollutants in biological fluids, and exploring molecular vibrations.
The new method leverages the coupling of visible-frequency single-photon sources to crystal lattice vibrations, known as phonons. By enhancing specific optical transitions, a phonon mode can be prepared in a quantum state and converted into a single MIR photon using a designed antenna. This approach could produce single MIR photons on demand, adaptable to various existing single-photon sources in two-dimensional materials, nanocrystals, and molecular systems.
This advancement could lead to the development of quantum technologies in the MIR frequency regime, potentially leading to more precise molecular studies and the development of efficient drugs for a healthier future.
Visit by collaborator Dr. Jelena Sjakste, Ecole Polytechnique, France
While visiting, Jelena Sjakste gave an inspiring talk on 'Density Functional Theory (DFT) and Density Functional Perturbation Theory (DFPT) for ultrafast dynamics of hot carriers and heat transport'.
We greatly value the opportunity to exchange ideas with Jelena and gain deeper theoretical insights to complement our work in materials science and nanofabrication. These discussions are essential for bridging the gap between theory and experiment. We explored new directions for our collaboration, aiming to combine theoretical insights with experimental validation to advance the material platform for photonic applications.

8th International Workshop on the Optical Properties of Nanostructures
Christian Ruiz and Elizaveta Semenova attended the '8th International Workshop on the Optical Properties of Nanostructures' hosted by the University of Münster, Germany. Christian presented a poster on 'Deterministic fabrication of quantum dots operating in telecom C-band'. Elizaveta gave an invited talk on 'From quantum dots to quantum networks: Scalable photonic devices operating in the telecom C-band'
 .
.
23rd International Winter School on New Developments in Solid State Physics
Michelle Wang, Valdemar Bille-Lauridsen and Elizaveta Semenova attended the 23rd International Winter School on New Developments in Solid State Physics, Mauterndorf, Austria.
Michelle presented a poster on relative higher-order band topology, focusing on inversion-symmetric Weyl semimetals, which host two distinct topological phases. Using a tight-binding model, she studied the interface between these phases and demonstrated the emergence of a conducting state localized along the 1D hinges. This result suggests a second-order topological distinction between the two semimetallic phases, analogous to that of an axion insulator.
Valdemar’s poster dealt with the theoretical limits of light-matter coupling strength between a dielectric cavity and a quantum dot. Here, a system consisting of a bowtie cavity coupled to a single quantum dot is explored. Valdemar has shown how the light-matter coupling strength scales with the system geometry and what will ultimately limit the achievable coupling strength.
Elizaveta gave an invited talk 🎙on ‘Scalable quantum photonic devices for telecom applications’.
Mauterndorf has a strong tradition of high-level scientific discussions with scientists actively contributing to discussions on the latest advancements in the field. Another tradition is skiing.

Meeting with Margrethe Vestager
Recently, DTU’s new chair of the board of governors, Margrethe Vestager, met with NanoPhoton member Elizaveta Semenova to learn about Elizaveta’s research. They discussed key topics that shape our research environment, from advancing cutting-edge research and strengthening interdepartmental collaborations to addressing challenges in the PhD programme and tackling gender balance in academia.

Welcome to new colleagues
In January and February we have welcomed two new postdocs, Baptiste Lefaucher and Marek Mikulicz. Baptiste will work on the development of quantum dot-based photon sources in the telecom C-band for integrated quantum photonics on the silicon nitride platform, and experimental characterization of intensity noise in integrated nanolasers. Marek's research focuses on integration of QD-based single-photon sources with photonic platforms and on template-assisted selective epitaxy which enables the monolithic integration of III−V-based active photonic components, such as photodetectors and lasers, onto silicon via a flexible CMOS-compatible process.

Tutorial at the 3rd Quantum Optics and Nanophotonics Winter School, Sheffield, UK
Elizaveta Semenova attended the 3rd Quantum Optics and Nanophotonics Winter School, organized by the University of Sheffield, UK. The school brought together experts with exceptionally high scientific levels. Elizaveta had the privilege of giving a tutorial on topics we explore in NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics and in the QPIC 1550 EU project.

External stay at MIT, USA
Beñat Martinez de Aguirre Jokisch, spent the fall semester last year at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the USA.
During his external stay, Beñat was part of the Nanostructures and Computation group at MIT, working under the supervision of Professor Steven Johnson. The collaboration aims to explore novel topology optimization techniques with applications to nanolaser technologies.

Paper in Physical Review Letters
We are devoted to exploring deep sub-wavelength light confinement to boost the optical field strength and, thereby, the interaction with active materials, such as quantum dots. We have come a long way towards mastering the design and engineering of optical cavities with extreme dielectric confinement, but the better we get at confining light at the nanoscale, the harder it becomes to precisely place a quantum dot in the optical hot spot.
In our paper 'Lithographically defined quantum dot with subwavelength confinement of light', we propose the use of a single etching step to define optical cavities with built-in quantum dots by nanostructuring of a semiconductor membrane with embedded quantum wells. The work - which originated as a student project at DTU Electro - combines quasinormal mode theory of Maxwell's equations and the effective mass Schrödinger equation to design, model, and optimize the light-matter interaction in a lithographically defined quantum dot with subwavelength confinement of light.
On the front cover of ACS Photonics
Our recent article on ‘Omnidirectional Gradient Force Optical Trapping in Dielectric Nanocavities by Inverse Design’ made it to the front cover of ACS Photonics.

Modeling light-matter interaction at the nanoscale
Designing the hardware for tomorrow's quantum information technology relies on efficient and transparent tools for modeling light-matter interaction at the nanoscale.
Using quasinormal mode-theory, we have developed one such tool, namely a new approach to calculate the coupling strength of quantum emitters in general electromagnetic resonators. We then applied it to analyze strong coupling between a quantum dot and an optical cavity with deep subwavelength confinement, and comparing to reference calculations, we find an extraordinary agreement to better than one part in ten thousand!
For details, check out the paper in Physical Review B.

Maria Vittoria Gurrieri defended her PhD thesis
On 29 November Maria Vittoria successfully defended her PhD thesis on ‘Polariton Dynamics in Ultra-Confined Optical Cavities: A Study of Interaction Effects and Coherence Properties’.

NanoPhoton lecture by Dr. Fabrice Laussy on 28 November
Dr. Fabrice Laussy, the Material Science Institute of Madrid, ICMM-CSIC, Spain, will give a lecture on 'Concepts and Theories of Quantum Light Sources' on 28 November at 13:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
We will discuss the general understanding of quantum light sources, starting with the single-photon emitter, and argue that well well-known examples constitute but a tiny and slippery tip of the iceberg. We will be interested, in particular, in why one does not (yet) have perfect single single-photon sources in the sense that one has perfect (so so-called super super-) conductors or perfectly non non-viscous flow (superfluids). More generally, we will adopt a strongly quantum quantum-mechanical stance that observation is at the centre of any quantum quantum-optical phenomenon and that what is usually measured is severely biased by our classical intuition, thereby overlooking the most interesting emission, of unsuspected complexity, even in the simplest possible systems. A specific claim that one should turn to at least three three-photon correlations to pass a threshold of quantum complexity (non non-Gaussian states), even when dealing with single single-photon
sources, will be presented and supported by experimental evidence for the first time. This will bring us towards a final discussion on the theoretical panorama that subtends these conceptual perspectives.
---
The talk provided a new and very interesting perspective on the fundamental quantum noise properties of single-photon sources.
Invited paper out in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics
We have an invited paper out in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics: 'Nanostructured Semiconductor Lasers'.
The paper presents recent theoretical and experimental progress on different types of nanolasers, including photonic crystal lasers, lasers with extreme dielectric confinement and Fano lasers.
NanoPhoton lecture by Professor Tomasz Czyszanowski on 20 November
Professor Tomasz Czyszanowski, Lodz University of Technology, Poland, will give a lecture on 'Lasing from true bound states in the continuum cavity compatible with standard semiconductor technology' on 20 November at 11:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
Laser cavities based on bound states in the continuum (BICs) can be achieved using configurations composed of a high refractive index periodic structure embedded in significantly lower refractive index surroundings, enabling vertical confinement of the grating modes. To date, BICs have been observed in photonic crystal slabs sandwiched between a substrate and superstrate of the same refractive index (vertical symmetry), making them technologically challenging and incompatible with standard semiconductor technology due to the membrane configuration or dielectric substrates.
In the presentation he will introduce the fundamentals of BIC-cavity with DBR design and illustrate its operation with characteristics of lasing properties, including nonlinear behavior, photon statistics, beam spatial distribution, and vortex occurrence. The configuration combines a high degree of design freedom with the realization of very high-quality factor cavities in conventional semiconductor technology, paving the way for electrically driven devices.
---
The talk explained the physics of the various confinement mechanisms in grating-based structures and how to manipulate and exploit the phenomenon of bound states in the continuum. A special focus was on structures which can be integrated with standard semiconductor technology, i.e. VCSEL-like structures, where he showed both experimental and theoretical results of promising configurations. Thank you very much for the interesting and inspiring talk.

Annual follow-up with the DNRF
In the beginning of November, we had our annual follow-up meeting with two board members and the CEO of the Danish National Research Foundation - DNRF.
On the agenda was a presentation of centre activities and achievements of the past year and our expectations for the future presented by our centre leader, Jesper Mørk.
Two members, Meng Xiong and Frederik Schröder, gave talks on ‘Room temperature continuous wave operation of InP EDC nanolasers’ and ‘Strong light-matter interactions in dielectric nanocavities coupled to 2D materials’, respectively.

Welcome to Dayang Li
Dayang Li, postdoc, joined NanoPhoton on 1 November. Dayang will work on numerical simulation and optical characterization of extremely confined non-radiative states in nanocavities, including anapole states and bound states in a continuum.

And the 'Best Student Presentation Award' goes to Benjamin Gøtzsche
Benjamin Gøtzsche received the ‘Best Student Presentation Award’ at the SPIE Optics + Photonics 2024 in San Diego. The Conference Chairs of SPIE Optics + Photonics conference found that Benjamin’s presentation entitled ‘All-dielectric self-induced back-action trapping’ was “outstanding”.

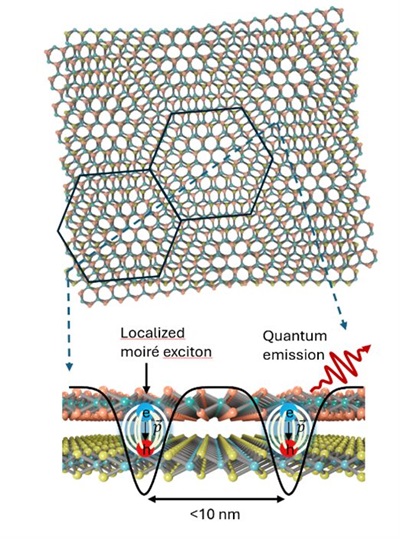
Groundbreaking paper in Nature Communications
The paper 'Moiré-engineered light-matter interactions in MoS2/WSe2 heterobilayers at room temperature' showcases a significant breakthrough in quantum 2D materials.
The key findings are:
Moiré Potential: For the first time, we demonstrate the significance of moiré potential at room temperature due to atomic reconstruction, evidenced by a substantial large twist-angle-dependent energy shift (>200 nm) of interlayer excitons.
Device Applications: Integrating moiré superlattices with silicon single-mode cavities has led to devices with much lower light emission thresholds, an order of magnitude smaller compared to those using delocalized interlayer excitons.
The findings underscore the exceptional potential of moiré superlattices in manipulating light-matter interactions at room temperature, paving the way for advancements in energy-efficient photonic and quantum devices.
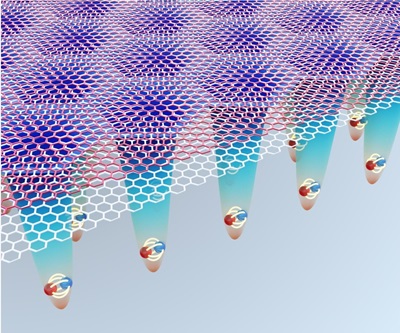
Sanshui Xiao awarded the Villum Experiment grant
The project’s objective is to create innovative optical microscopy with superior spatial resolution for exploring quantum physics within moiré superlattices. By stacking two-dimensional materials with a slight twist, researchers create moiré patterns that lead to unique electronic and optical properties. Quantum technologies have the potential to provide enormous advancements in massive applications, including ultra-secure communications, highly sensitive metrology, and super-fast computing. A central building block for quantum technologies is a single-photon emitter. One of the biggest challenges is generating purely identical quantum light sources with indistinguishability and fidelity close to unity, ideally operating under elevated temperatures.
If successful, the outcome would provide a new platform for generating purely identical quantum light sources, making a huge impact on quantum communication and quantum information processing.
Paper in ACS Publications
We have a paper out on 'Omnidirectional Gradient Force Optical Trapping in Dielectric Nanocavities by Inverse Design'.
We have developed new designs for optical traps using integrated dielectric nanocavities. These traps can capture single subwavelength particles or molecules in all directions, solely based on optical gradient forces. These results have just been published in ACS Photonics and may find applications in biomolecular analysis, levitated cavity optomechanics, and cold atom physics, moving us closer to integrated bio-nanophotonics and quantum mechanical experiments.
A new research assistant in NanoPhoton
Thor Weis, who joined us on 1 October, will work on design, fabrication, and characterization of nanoelectromechanical systems. These can be integrated with silicon photonics to produce tunable photonic devices and reconfigurable photonic circuits.

NanoPhoton workshop
In the beginning of September we went off for our annual workshop. We spent two days with inspiring talks, interesting discussions and lively poster sessions. We touched on work already carried out, our present projects and opportunities and ideas for the future. It was great to spend time together and experience the strong motivation and commitment of our members.

We welcomed Nikolaj Balslev Hougs in July
On 1 July we welcomed PhD student Nikolaj Balslev Hougs. Nikolaj’s research is focused on light-matter interaction and (extreme) dielectric confinement of light, especially promoting the former via the latter. This includes both design, fabrication and characterization of devices wherein this is possible.

Inaugural lecture by Professor Martijn Wubs
In an auditorium full of friends, family and colleagues, Martijn gave his🎙 inaugural lecture entitled ‘Light and layers for tomorrow’s technology: Quantum Nanophotonics and 2D materials’. In his talk, Martijn outlined the possibilities to influence quantum optical processes by engineering the nanophotonic environment of quantum emitters such as quantum dots, atoms and colour centres. Examples are spontaneous emission, collective emission, and energy transfer. He then discussed novel types of quantum emitters in two-dimensional materials studied in his group, as potential light sources in future technology. He ended with nanophotonic cavities, which his group studies for two reasons: first to make light sources bright and spectrally pure, and second for on-chip trapping of small particles and molecules by optical forces.

Ali Nawaz Babar defended his PhD thesis
On 20 August, Ali Nawaz Babar successfully defended his PhD thesis on 'Fabrication and characterization of silicon photonic cavities with atomic-scale confinement'.
Paper in Laser & Photonics Reviews
The paper 'The Onset of Lasing in Semiconductor Nanolasers' suggests a new definition of the laser threshold valid in the entire range from macroscopic lasers to nanolasers. For nanolasers exploiting deep sub-wavelength confinement of light, the recycling of photons needs to be taken into account. An extensive comparison is made to other threshold definitions.

New paper out in Physical Review A
In the paper 'Self-pulsing dynamics in microscopic lasers with dispersive mirrors', we demonstrate how integrating a passive dispersive reflector into a semiconductor laser can tailor laser dynamics to generate ultrashort pulses and achieve stable dual-mode lasing. A key highlight is the derivation of a generalized characteristic equation for relaxation oscillations, explicitly accounting for frequency-dependent mirror losses. This model is then applied to a coupled-cavity Fano laser, showcasing its potential for customizing mirror dispersion for self-pulsing.
NanoPhoton lecture by Otto Moensted Visiting Professor Martin van Exter on 13 June
Professor Martin van Exter, Leiden University, the Netherlands, will give a lecture on 'Micro- and nanocavity resonances: experiments and their analysis with a classical input-output formalism' on 13 June at 11:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
Optical micro- and nanocavities can trap light in small volumes and enhance the light-matter interaction of intra-cavity emitters.The analysis of these cavities typically uses resonance spectroscopy, which probes the cavity output as a function of the optical frequency (and possibly the alignment) of the optical input or the internal fluorescence. We have performed these experiments on Fabry-Perot-type microcavities at Leiden University and on extreme dielectric confinement (EDC) cavities at DTU - Technical University of Denmark. We will present the results of both experiments and their analysis with a classical input-output formalism, which combines a Green’s tensor description of the microcavity with a modal decomposition (= eigenmode analysis) of this tensor.

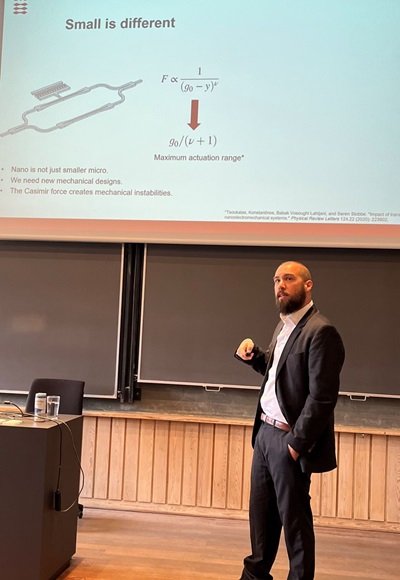
Konstantinos Tsoukalas defended his PhD thesis
Konstantinos Tsoukalas successfully defended his PhD thesis on 'Quantum Vacuum Fluctuations in Nanoscale Devices' on 10 June.

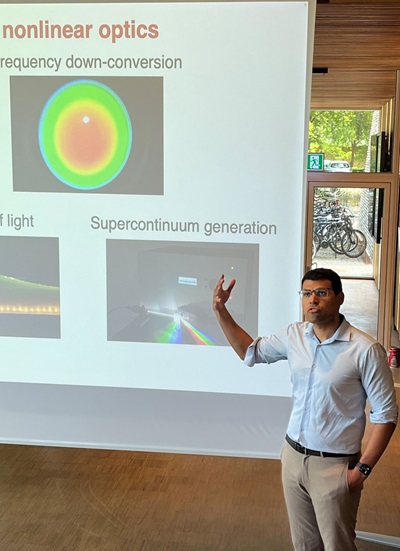
NanoPhoton lecture by Nicholas Rivera on 4 June
Nicholas Rivera Junior Fellow,Harvard University, USA, will give a lecture on 'Controlling quantum noise through nonlinear optics, and understanding nonlinear optics through quantum noise' on 4 June at 13:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
The statistical properties of electromagnetic fields – the subject of quantum optics – are of great practical importance and fundamental interest. In this talk, Nicholas Rivera will cover some of their recent endeavors in quantum optics, which are concentrated in two directions: (1) using nonlinear optical effects to reduce fluctuations of light, (2) and using quantum noise as a way to probe and understand complex nonlinear interactions.
Along the lines of the first part, he will theoretically show how designing certain types of nonlinear filters and lasers can enable the deterministic creation of fundamental quantum states of light such as many-photon Fock states and Schrodinger cat states, at optical frequencies. In the second part, he will show experiments revealing how quantum noise can be used as a sensitive probe of ultrafast nonlinear dynamics, even when conventional measurements of averaged quantities show only weak signatures of the dynamics. Rivera will also show how
their noise-measurement framework reveals a surprising effect in which a femtosecond pulse of light can completely reject added noise in a large number of degrees of freedom, even when those degrees of freedom are chiefly responsible for driving the mean-field dynamics.
He will conclude by describing a few avenues anticipated by this work, such as making optical amplifiers which could noiselessly amplify, and developing new tools for understanding complex nonlinear optical systems such as strongly multimode fibers.

Inaugural lecture by Professor Søren Stobbe
On 31 May, Søren Stobbe gave his inaugural lecture entitled “Photonic Nanotechnology”. In his talk, Søren outlined recent developments in the field of photonic nanotechnology relying on silicon nanodevices with unprecedented dimensions, ranging from fundamental research on photonic cavities with unparalleled single-photon intensities and photonic topological insulators to innovation-driven research on programmable photonics and chip-scale spectrometers

Publication in Physical Review B
In our publication 'Carrier diffusion in semiconductor nanoscale resonators', we show that nanoscale optical resonators with deep sub-wavelength light confinement strongly accelerate the diffusion of electron-hole pairs. This is important for understanding the dynamics of nanocavities and offers new possibilities for designing ultra-fast all-optical switches.
Paper out in Nature Communications
We had our latest research on 'High-throughput quantum photonic devices emitting indistinguishable photons in the telecom C-band' published.
We not only demonstrated quantum dot-based sources of single photons of high purity and indistinguishability operating in the telecom C-band, but also developed a technique that allows them to greatly enhance the device fabrication yield, reaching ~30%. This breakthrough makes it possible to overcome key limitations in scalability of quantum communication and information technologies and opens up new possibilities for advanced quantum networks in the telecom range.
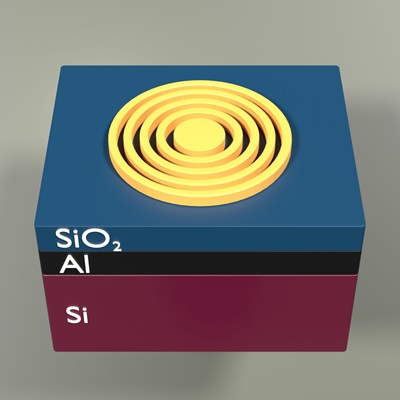

Paper in Optics Express was Editor's pick
Our paper on 'Heterogeneous integration of single InAs/InP quantum dots with the SOI chip using direct bonding', published in Optics Express, was highlighted as an Editor's Pick.
An integrated silicon chip is a great host platform for photonic quantum information processing. However, silicon cannot emit light, which requires the integration of active material to benefit from all the advantages that advanced silicon processing provides. Now, NanoPhoton researchers in collaboration with researchers from Wrocław University of Science and Technology
have demonstrated hybridization of single InAs/InP quantum dots and Si platform for coupling single photons at telecom. We show the efficient transfer of single photons to the Si waveguide - a major achievement in the development of silicon quantum integrated circuits. The new method offers cost-effective scalability in setting up a multi-source environment for quantum photonic chips.
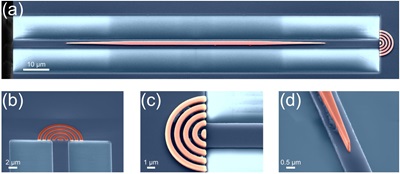
Pawel Holewa receives award
Paweł Holewa is recognized as one of the top 100 young scientists in Poland under 30 by the FNP Foundation for Polish Science. The START program is the oldest scholarship program in Poland for the best young scientists.

Kirsten Moselund, appointed adjunct professor at DTU Electro, collaborates with NanoPhoton
In her inaugural lecture, Kirsten Moselund gave an insightful perspective on the important and emerging topic of hybrid III-V/silicon photonics. She covered research done at her former workplace, IBM in Zürich, as well as the focus of her present activities as a Professor at EPFL and the the Paul Scherrer Institute. An important topic is the development of novel epitaxial techniques for monolithic integration of III-V semiconductors on silicon. Moselund covered waveguide-coupled high-speed III-V photodetectors, a collaboration with NanoPhoton, and III-V photonic crystal lasers on silicon for on-chip optical communication.

Göktug Isiklar defended is PhD thesis
Göktug Isiklar successfully defended his PhD thesis on 'Topology Optimization Approaches for Nanophotonic Applications' on 26 April.

The Science Festival "Forskningens Døgn"
In April, NanoPhoton took part in the science festival “Forskningens Døgn” again. We met children, students and adults who were curious to learn about our research in nanophotonics at events at DTU and Videnskabernesselskab, respectively. Our experiments with lasers, grapes, and other exciting devices helped explain what we do, as did tours of our labs.


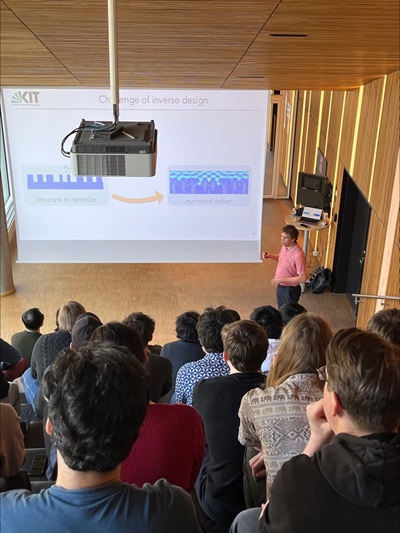
NanoPhoton Lecture by Carsten Rockstuhl on 25 April
Professor Carsten Rockstuhl, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany, will give a lecture on 'Information-driven Computational Nanophotonics' on 25 April at 15:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
For a long time, computational nanophotonics dealt with developing suitable tools that solve Maxwell’s equations and study how the optical response of a given structure will be. In more recent times,
however, the focus of attention has shifted to the opposite. Nowadays, we ask how a structure should look to offer an optical response on demand. Fueled by the recent development in computer science, information-driven approaches based on artificial intelligence and the notion of fully differentiable programming have triggered an immense impetus. In this talk, Rockstuhl will discuss selected approaches to solving inverse problems in the design of photonic nanostructures and discuss some examples that are shamelessly biased toward our contributions. He will also touch upon the notion of a digital twin in the context of photonic material design and outline a comprehensive modeling approach for macroscopic photonic devices made from molecular materials.
---
The talk gave a very nice introduction to various optimisation strategies for nanophotonic systems design - in particular with regards to designing advanced 3D structures to be realised using 2-photon lithograhy.

Talk at the PIERS 2024 conference in Chengdu, China
Professor Søren Stobbe presented our recent results on subdiffraction dielectric cavities at the hot topics session at the PIERS 2024 conference in Chengdu, China.

NanoPhoton Lecture by Riccardo Sapienza on 16 April
Professor Riccardo Sapienza, Imperial College, London, UK, will give a lecture on 'From spatial nanophotonics to temporal one, the case for time-varying metamaterials' on 16 April at 11:00 at 341/023.
Metamaterials have revolutionised the way we control light transport and generation. Yet, to date, they rely on passive architectures, only redistributing incident wave energy - for example in a metalens, or a photonic crystal cavity - with no power to break time-reversal symmetry and energy conservation. Here, Sapienza will discuss their first steps towards driven photonic systems, able to convert energy to function and reach advanced functionalities. Firstly, he will discuss their experiments with dielectric nano-cavities designed around an individual emitter [1], then he will move the observation of the temporal analogue of Young’s double slit experiment, performed in a time-varying metamaterial [2]. This is an ITO multilayer whose reflectivity can be changed abruptly, on the time of the light optical cycle.
References:
[1] Fluorescence enhancement in topologically optimized gallium phosphide all-dielectric nanoantennas, Cynthia Vidal, Benjamin Tilmann, Sunny Tiwari, TV Raziman, Stefan A Maier, Jerome Wenger, Riccardo Sapienza, Nano Letters 24, 2437 (2024).
[2] Double-slit time diffraction at optical frequencies, Romain Tirole, Stefano Vezzoli, Emanuele Galiffi, Iain Robertson, Dries Maurice, Benjamin Tilmann, Stefan A Maier, John B Pendry, Riccardo Sapienza, arXiv:2206.04362, Nature Physics (2023).
---
The talk provided wonderful insights into the design and physics of nanocavities and their possible applications.
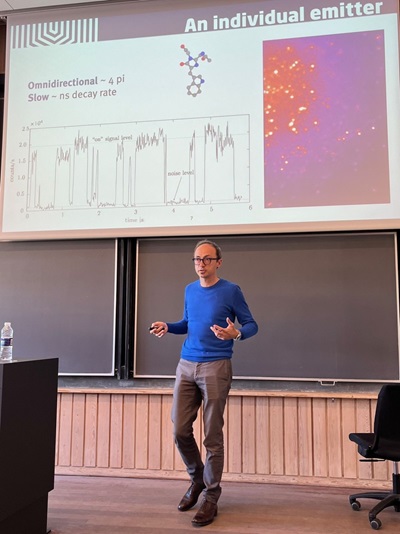
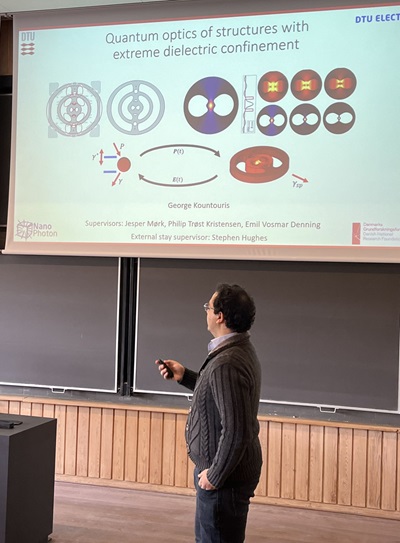
George Kountouris defended his PhD thesis
On 15 April George Kountouris successfully defended his PhD thesis on 'Quantum optics of structures with extreme dielectric confinement'.
New colleagues
From January to April we received a number of new colleagues.
Valdemar Bille-Lauridsen, PhD student, studies nanobeam structures and the extreme confinement of light.
Mattias Rasmussen, Postdoc, works on optical and electrical characterization of photonic integrated circuits designed to explore the linear and nonlinear interactions between light and matter.
Karolina Połczyńska, Postdoc, works on a project that tackles key challenges in quantum photonics, including efficient light coupling between different components and minimizing signal processing losses.
Hanlin Fang, Postdoc, focuses on the exciton physics in 2D materials and their use in advancing integrated optophotonic applications.
Corné Koks, Postdoc, studies single photon emitters in hBN and look at their spectroscopic and temporal properties to get insights both of the origin and the environment of the emitters.
Monia Runge Nielsen, Postdoc, will use advanced electron microscopy to image light-induced charge carrier accumulation in photocatalysts.

NanoPhoton turns 4
On 1 April, 2024 we celebrated NanoPhoton's 4-year birthday.

NanoPhoton Lecture by Kristinn B. Gylfason on 21 March
Professor Kristinn B. Gylfason, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden, will give a lecture on 'Photonic MEMS in Silicon and 3D-printed Silica Glass for Programmable Photonic Circuits and Sensing' on 21 March at 11:00 at 341/022.
Photonic integrated circuits (PICs) promise to be the optical equivalent of electronic integrated circuits (ICs). However, current PICs fall far short of electronic ICs in terms of the number of devices per chip. One roadblock is the power consumption and the footprint of active photonic components. By micromechanical actuation of PICs, we show orders of magnitude reduction of power consumption compared to current thermo-optic counterparts. We demonstrate our approach by implementing MEMS tunable photonic devices such as phase shifters, couplers, and wavelength filters. We realize our technology in a silicon photonics foundry platform and show complex circuits on a small chip. Furthermore, we show wafer-level vacuum-sealing of the silicon photonic MEMS circuits.
---
In his talk, Kristinn explained about the latest developments in his group, spanning across graphene thermal emitters, CO2 detectors, and nanoelectromechanical silicon photonic.

News & Views article in Nature Physics
Martijn Wubs wrote a News & Views article 'Multiphoton quantum statistics from scattered classical light' in Nature Physics. It is about a recent publication 'Nonclassical near-field dynamics of surface plasmons', also in Nature Physics, by Mingyuan Hong and co-workers from the Quantum Photonics Group of Louisiana State University.
Paper chosen for OPTICA's Spotlight on Optics
The paper 'Topology Optimization Framework for Designing Efficient Thermo-Optical Phase Shifters' received a comprehensive review which encapsulates the essence of our research. It highlights how topology optimization is leveraged to craft high-performance optical phase shifters, that can outperform other state-of-the-art devices. These phase shifters are meticulously designed to address crucial parameters such as low loss, minimal power consumption, enhanced speed, compact footprint, and fabrication complexity. The derived framework can be used to design phase-shifters for different applications, ranging from optical transceivers, light ranging and detection, quantum information processing and neural networks, among others.
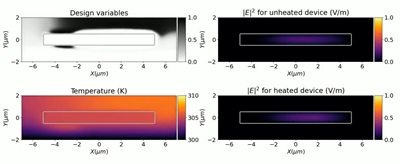
Paper on 'Optical bistability and flip-flop function in feedback Fano laser' in Optics Express
We have theoretically demonstrated that incorporating strong optical feedback into a Fano laser can realize optical bistability, mirroring the functionality of electrical flip-flops for optical signal processing applications. Unlike traditional optical bistable devices that rely on changing the susceptibility of a nonlinear medium—often leading to large sizes, high energy use, or slow switching—our feedback Fano system leverages intense field localization within a nanocavity. This allows state switching by modulating the loss of one of the laser mirrors rather than altering the medium’s susceptibility. Such modulation, achievable locally on the nanocavity, facilitates rapid flip-flop actions with minimal energy requirements.
Prestigious 2024 DOPS award to Ali Nawaz Babar
Our NanoPhoton member Ali Nawaz Babar was honored with the prestigious 2024 DOPS award by the Danish Optical Society for outstanding contributions to Denmark's optics and photonics community. Ali's work not only pushes the boundaries of our knowledge but also serves as an inspiration for aspiring researchers, showcasing the epitome of cutting-edge research in the Danish optics community.

NanoPhoton lecture by Jacob Khurgin on 9 February
Professor Jacob Khurgin, Whiting School of Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, USA, will give a lecture on 'Why do the refractive indexes of different materials differ so little and are also so difficult to change?' on 9 February at 14:00 at LY340-R9.14.A/Line of Light.
For too long the functionality of optical devices and systems has been severely restricted by the very limited range of refractive indices at the disposal of designers. These limitations become especially constricting in the currently most active areas of optics – integrated photonics, photonic crystals, metamaterials and metasurfaces. A simple increase of the value of refractive index by 50% can result in disproportionally large improvement in performance (i.e. smaller size, less cross-talk, higher resolution, and so on, depending on application) With that in mind, Khurgin explores what are the fundamental limits that limit the scope of refractive indices as a function of wavelength, explain why higher index materials have not yet materialized and point out a few tentative directions for the search of these elusive materials, be they natural or artificial.
---
Jacob gave a very interesting perspective on the variation of the refractive index across a wide range of materials and the possibilities for modulating the refractive index. One of the important conclusions of his research is that the material used has less influence on the power required for modulating the index than the specific resonant or travelling wave scheme employed to enhance the interaction time between light and matter.

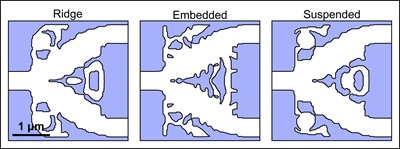
Work on topology-optimized power splitters in Materials for Quantum Technology
In this work with the title 'Inverse design and characterization of compact, broadband, and low-loss chip-scale photonic power splitters' the inverse design method of density-based topology optimization is used for power splitters to explore the potential for high performance in ultra-broad bandwidths. Designs are made for three different waveguide platforms - ridge, embedded, and suspended - in silicon. By utilizing high-resolution single-step electron beam nanofabrication, we successfully fabricate suspended power splitters and validate their performance through optical characterization, showcasing good alignment with our numerical results.
Scientific results published in ACS Photonics
Our scientific results on demonstrating the coherent on-demand generation of indistinguishable photons in the telecom C-band using single QD devices, published in ACS Photonics, focus on harnessing the power of InAs/InP epitaxially grown quantum dots as quantum light sources in the telecom C-band —an essential component for various applications in quantum communications compatible with integration via fibre-optical networks. The paper is entitled 'On-Demand Generation of Indistinguishable Photons in the Telecom C-Band Using Quantum Dot Devices'.
Paper in Optics Express
In our paper 'Experimental demonstration of a nanobeam Fano laser' we suggest and experimentally demonstrate what we believe is a new configuration of the Fano laser based on a nanobeam geometry. Compared to the conventional two-dimensional photonic crystal geometry, the nanobeam structure makes it easier to engineer the phase-matching condition that facilitates the realization of a bound-state-in-the-continuum (BIC). We investigate the laser threshold in two scenarios based on the new nanobeam geometry.
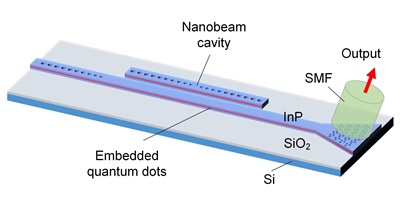
Paper in Optical Materials Express selected editor's pick
Our paper 'Experimental realization of deep sub-wavelength confinement of light in a topology-optimized InP nanocavity' was published in Optical Materials Express and selected editor's pick. It introduces a new class of cavities featuring extreme dielectric confinement (EDC) into the realm of III-V semiconductors, offering order-of-magnitude Purcell-enhancement of the radiative rate. EDC nanocavities may be employed to significantly improve the properties of nanolasers, nanoLEDs and single-photon sources, among other applications.

Shih Lun Liang defended his PhD thesis
On 18 January, Shih Lun Liang succesfully defended his PhD thesis 'Dynamics of photonic crystal nanolasers based on Fano resonance'.
NanoPhoton in Snowbird, Utah
The Winter Colloquium on the Physics of Quantum Electronics (PQE) took place in the beginning of January. It is a fantastic conference, arranged for 53 years by one of the true pioneers of quantum optics, Prof. Marlan O. Scully. The conference focuses on quantum optics, laser physics and light-matter interactions.
From NanoPhoton, we were honoured to give a plenary talk on our work on semiconductor nanolasers, presented by our centre leader Jesper Mørk.

New professors in NanoPhoton
Our members Martijn Wubs and Søren Stobbe, were appointed full professors as of 1 January 2024.
Martijn Wubs’ research field is nanoscale quantum optics, where he studies quantum emitters and the propagation of quantum states of light in nanostructured environments. His group focuses on novel types of light sources in and around two-dimensional materials, with possible applications in optical communication and quantum technology.
Søren Stobbe's research is centered around understanding the properties of semiconductors at the deep nanoscale and exploring their innovation potential for applications in photonic nanotechnology.


Welcome to Odysseas Kosmatos
On 1 November we welcomed Odysseas Kosmatos. Odysseas will do a PhD Project on “Selective epitaxy of III/V Si nanostructures for photonic application”. It is about theoretical and experimental investigation of nucleation processes of III-V compounds on silicon. Developing and applying new epitaxial methods for realizing III-V photonics devices monolithically integrated into the Si-platform. The project is carried out in collaboration with École Polytechnique.

NERD grant to Nicolas Stenger
Nicolas Stenger was awarded the Novo Nordisk New Exploratory Research and Discovery (NERD) Program. It is a 14 MDKK grant that runs for seven years.
Quantum emitters are key in developing light-based quantum technology. In this project, we will explore in detail the interaction of quantum emitters with noise in the environment due to atomic vibrations. The noise generated by these vibrations destroys the useful quantum properties of the quantum emitter. Finding ways to mitigate the influence of vibrations could enable the possibility to create quantum emitters robust to thermal vibrations and to work close to or at room temperature. This could allow the future development of quantum technologies without the use of power-hungry cooling systems and potentially facilitate their large-scale use in our society.

Visit from Taiwan
Recently, a delegation from Taiwan, including companies and national research centres, visited DTU to learn about the Danish quantum ecosystem. On this occasion, our member Elizaveta Semenova presented the research we carry out within NanoPhoton.

Talk by guest PhD Junhyeong Kim
In October, we have a guest PhD student, Junheyong Kim, visiting us from KAIST - Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology, Daejeon. Junhyeong gave a presentation about his research on using "AI in nanophotonics for design and computing".

Two new PhD students
We welcomed two new PhD students, Michelle Wang and Matias Bundgaard-Nielsen.
Michelle's research focuses on topological phenomena in photonic systems. She studies photonic band structures using the language of group representations, with potential applications for photonic crystal design. Matias will be working on a deep theoretical understanding of the quantum optics of nanostructures with Extreme Dielectric Confinement (EDC), including developing efficient numerical simulation tools. He will work on identifying promising structures for experimental exploration by investigating, e.g., nanolasers with reduced quantum noise.

Talk by Nir Rotenberg, Queen’s University, Canada
Associate Professor Nir Rotenberg from Queen’s University, Canada, gave a NanoPhoton Lecture on “Linear and nonlinear photonic quantum circuits”. Nir gave a fascinating talk about the perspectives on using quantum dots for quantum information processing, emphasizing the physics and the pros and cons of quantum dots for this application.
The Micro and Nano Engineering (MNE) conference 2023 in Berlin
Our NanoPhoton members Bingrui Lu, Ali Nawaz Babar, Guillermo Arregui Bravo, and Søren Stobbe presented their work in Berlin. Bingrui Lu talked on “Design and All-In-One Etch of Silicon Metalens for Near-Infrared Focusing”. Ali Nawaz Babar on “Integrating top-down nanopatterning with bottom-up self-assembly to fabricate photonic cavities with atomic-scale dimensions”. Guillermo Arregui Bravo on “Bowtie photonic-crystal waveguides as strong light-matter interfaces”.

Congratulations to our PhD student Qiaoling Lin
Qiaoling Lin successfully defended her PhD thesis. The thesis title is “Exploring excitons in van der Waals heterostructures and their potential for lasing”. Prof. Uriel Levy (The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel) and Prof. Harri Lipsanen (Aalto University, Finland) were the external examiners. The proud Nanophoton supervisors were Sanshui Xiao (main), Nicolas Stenger and Martijn Wubs.

Michael Seifner was awarded a Villum Experiment grant
The Villum Experiment Programme was created for research projects that challenge the norm and have the potential to fundamentally change the way important topics are approached. The granted project with the title "Nanoscale Imaging of a Photocatalyst at Work: What Comes After the Light?" will focus on the nanoscale imaging of charge carrier accumulation in defined nanoparticle photocatalysts upon light irradiation inside a transmission electron microscope. A successful implementation of the project could help better understand the fundamental processes involved in photocatalytic reactions.

Visit from the DNRF
The DNRF visited us for our annual follow-up meeting. As usual, hosting and presenting our research and ideas to the foundation was a great pleasure. We greatly appreciate the positive atmosphere of these meetings and the supportive approach of DNRF.

Keynote lecture at FEMS EUROMAT 2023
Michael Seifner, gave a keynote lecture at FEMS EUROMAT 2023. The conference focused on the latest materials science and technology advancements. The talk dealt with mapping the electric field in topology-optimized photonic cavities with extreme dielectric confinement using scanning transmission electron microscopy in combination with electron energy loss spectroscopy.

Our annual NanoPhoton workshop in September
At our annual workshop we spent two days together presenting our research, exchanging ideas, discussing the way forward and enjoying being together. It was indeed a good and enriching experience. Thank you all for joining and contributing to this.

Visit from the University of Würzburg, Germany
Professor Sven Hoefling from the University of Würzburg, Germany, visited us and gave a talk on “Semiconductor quantum dot based quantum technologies”. It was a great overview of the science and technology of semiconductor quantum dots and their possible applications within quantum technology. The group in Würzburg has made several seminal contributions to the field, and it was great to discuss with one of the pioneers.

We broke the world record
We are proud to share that a group of NanoPhoton members recently published an article in Optica demonstrating a photonic crystal nanolaser with a record-low threshold current of 730 nA at room temperature.
Such nanolasers push the boundaries of laser miniaturization and are ideal candidates for on-chip applications, where low-loss links replace energy-consuming electrical interconnects. The lasers can be modulated at 3 GHz with an energy cost of only 1 fJ/bit.
Congratulations to the authors: Evangelos Dimopoulos, meng xiong, Aurimas Sakanas, Andrey Marchevsky, Gaoneng Dong, Yi Yu, Elizaveta Semenova, Jesper Mørk, and Kresten Yvind.
Participation iNOW 2023 in Würzburg, Germany
Our NanoPhoton member Alisha Nanwani participated in the International Nano-Optoelectronics Workshop (#iNOW) 2023 in Würzburg, Germany and presented her results on "Selective area epitaxy of InP/InAs/InP on Silicon(001)".

Congratulations to Nikolaos and Kasper
Our two master's students Nikolaos Chatzaras and Kasper Spiegelhauer successfully defended their master’s thesis ”Characterization and simulation of electrically-driven microlasers”.

Participation in the workshop FAME in Cork, Ireland
Yury Berdnikov and Elizaveta Semenova attend the workshop FAME in Cork, Ireland, and present NanoPhoton results on “Droplet mediated epitaxy“ and “Fine-tunable near-critical Stranski-Krastanov growth of InAs/InP quantum dots”.

Paper published in Physical Review Letters
Our paper “Stochastic Approach to the Quantum Noise of a Single-Emitter Nanolaser” was published in Physical Review Letters. Surprisingly, a simple and easy-to-implement generalisation of standard laser rate accounts for the full intensity quantum noise of a nanolaser. Link in the comment field.
The paper is authored by NanoPhoton members Matias Bundgaard-Nielsen, Emil Denning, Marco Saldutti, and Jesper Mørk.
International Conference on Optics of Excitons in Confined Systems (OECS 18) in Lecce, Italy
Maria Vittoria Gurrieri and Paweł Holewa participated in the International Conference on Optics of Excitons in Confined Systems (OECS 18). They presented their recent results: Maria Vittoria on polariton dynamics of single-mode nanocavities and Pawel on the deterministic fabrication of quantum light sources.
OECS is a bi-annual conference that gathers scientists interested in the areas of optical excitations of semiconductors with specific attention on the physics of excitons, trions, and collective excitations in different materials and photonic nanostructures.

Congratulations to master's students defending their theses
Our three master's students Stefano Fornetti, Matias Bundgaard-Nielsen and Kamma Nørrelund Pedersen have defended their theses successfully. Stefano's thesis is entitled "Development of a quantum light emitter with controllable excitonic fine structure splitting", Matias' thesis "Modeling tools for quantum networks" and that of Kamma "Modeling of Photonic Quantum Information Processors".



From left to right: Stefano, Kamma, Matias
Visiting PhD student from Wroclaw University Science and Technology
PhD student Marek Burakowski from Wrocław University Science and Technology is joining NanoPhoton for six months for his external stay. His project is devoted to developing scalable fabrication methods for integrated quantum photonics.

NanoPhoton strongly represented at CLEO Europe 2023
A total of 11 NanoPhoton members are going to Munich, and we will do the following presentations including a keynote talk by our centre leader Jesper Mørk:
Monday
Jesper Mørk: “Semiconductor Nanolasers” (keynote talk), 8:30 hrs., room 4b ICM (EG-1.1)
Kristian Seegert: “Dual-mode lasing and beating oscillations in a microscopic laser based on electromagnetically induced transparency”, 9:15 hrs., room 13b ICM (CB-1.3)
Gaoneng Dong: “Ultrashort pulse generation using cavity-dumping in a Fano laser”, 9:30 hrs., room 13b ICM (CB-1.4)
Tuesday
Ayman Nassar Kamel: “All-Silicon Topology Optimized Two-Photon Absorption Detector for On-chip Interconnects”, 13:00 hrs., Hall B0 (EG-P.9)
Wednesday
Mikkel Heuck: “Proposal for Multiport Photon Routing using Photonic Crystal Cavity Phase Shifters”, 9:45 hrs., room 6 Hall B3 (B32), (CI-1.5)
George Kountouris: “A lithographically defined quantum dot with simultaneous sub-wavelength confinement of light”, 9:45 hrs., room 4a ICM (CK-4.5)
Thursday
Marco Saldutti: “Threshold with photon recycling in nanolasers with extreme dielectric confinement”, 14:15 hrs., room 13b ICM (CB-10.2)
Friday
Philip T. Kristensen: “Influence of surface roughness on the resonance frequencies and quality factors of optical cavities and plasmonic nanoparticles”, 11:15 hrs., room 21 ICM (EJ-4.4)
Mohammad Abutoama: “Semi-analytical Approach for Modeling Strong Coupling of Quantum Emitters in Electromagnetic Resonators”, 11:45 hrs., room 21 ICM (EJ-4.6)
Guillermo Arregui: “Backscattering in slow-light valley-Hall photonic topological waveguides”, 11:45 hrs., room 22a ICM 8 EC-2.5)
Meng Xiong: “Experimental realization of extreme light confinement in an InP nanocavity”, 17:15 hrs., room 4a ICM (CK-15.6)

Participation in World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization (WCSMO15) conference
Our NanoPhoton members, Beñat Martinez de Aguirre and Göktuğ Işıklar, presented their cutting-edge studies at the World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization (WCSMO15) conference.
Beñat talked on "Topology optimization of thermo-optical phase shifters". He shared his intensive studies on developing a multiphysics topology optimization algorithm for thermo-optics. By leveraging his methods, significant improvements in the efficiency and performance of optical phase shifters were achieved. Göktug’s talked on "Topology optimization of thermal initial value problems using a harmonic model". His presentation focused on reducing the computational cost of transient optimization problems while maintaining high device performance. His harmonic model approach showcased remarkable efficiency gains in tackling thermal initial value problems.


Visiting Professor from Leiden University
ofessor Martin van Exter from Leiden University is joining us for six weeks as an Otto Mønsted Visiting Professor at DTU Electro. He will give three NanoPhoton lectures on “Fine structure in resonance spectra of optical microcavities”, “Cavity quantum electrodynamics with semiconductor quantum dots”, and “Spatial quantum entanglement of photon pairs”, respectively., Prof. Van Exter has broad educational and management experience. He has been the educational director of Physics at Leiden University, and he is a co-developer of the MSc “Quantum Information Science & Technology”, a new joint Master's program of the Technical University of Delft and Leiden University.
Martin van Exter will return for another period of six weeks next year.

Compound Semiconductor Week 2023 at Jeju, South Korea
NanoPhoton was represented at the Compound Semiconductor Week 2023 at Jeju, South Korea, with a talk by our senior researcher Elizaveta Semenova on “Deterministic fabrication of single photon sources operating at the telecom C-band".

Evangelos Dimopoulos defended his PhD thesis
On 17 May, Evangelos Dimopoulos defended his PhD thesis on “Electrically-driven Photonic Crystal lasers”. Evangelos continues to work with us as a postdoc.

Paper on “Efficient low-reflection fully etched vertical free-space grating couplers for suspended silicon photonics”
NanoPhoton members Søren Engelberth Hansen, Guillermo Arregui Bravo, Ali Nawaz Babar, Marcus Albrechtsen, Babak Vosoughi Lahijani, Rasmus E Christiansen, and Søren Stobbe had their paper on “Efficient low-reflection fully etched vertical free-space grating couplers for suspended silicon photonics” published in Optics Express. The new grating coupler designed for suspended structures with low reflection and good coupling can be fabricated in a single-step lithography. It makes it ideal for testing new suspended nanophotonic devices such as compact dielectric bowtie cavities.
Rasmus E. Christiansen giving talks at Zuse and EPFL
NanoPhoton member Rasmus E. Christiansen recently gave two invited talks detailing research performed under NanoPhoton. The first talk was given at AMPD 2023 hosted by ZIB Zuse Institute Berlin and the second at Neuromorphic Photonics - Complex Lasers: from control to neuromorphic computation hosted by Swiss Photonics at École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne. Rasmus was invited to present central results from NanoPhoton detailing how to utilize photonic inverse design by topology optimization (#TopOpt, [1]) to enable experimental realization of unprecedented extreme dielectric confinement (#EDC) of light [2], to explore and map fundamental trade-offs between spatial and temporal light-confinement [3], to demonstrate the importance of selecting the appropriate confinement mechanism when designing EDC devices [4] as well as for a number of other applications of TopOpt to achieve extreme photonic device performance.
Links to references:
[1] Inverse design in photonics by topology optimization: tutorial (optica.org)
[2] Nanometer-scale photon confinement in topology-optimized dielectric cavities | Nature Communications
[3] On the trade-off between mode volume and quality factor in dielectric nanocavities optimized for Purcell enhancement (optica.org)
[4] Impact of figures of merit in photonic inverse design (optica.org)

CLEO in San Jose
At the CLEO conference in San Jose in May NanoPhoton presented some highlights from the work on nanostructured emitters, including the lowest threshold lasers ever realized. Our members gave talks on "Nanostructured Lasers for Femtojoule Photonics", "Experimental Demonstration of Photonic Crystal Nanolaser With sub-μA Threshold Current", and "Purcell-Enhanced Single-Photon Emitter Exploiting Extreme Dielectric Confinement" among other topics.


New PHD student joining NanoPhoton
On 1 May PhD student Christian Ruiz joined us in the centre. Christian will work on epitaxial growth of III-V semiconductor heterostructures. His research is focused on advancing self-assembled quantum dot growth methods and implementing new approaches to tailor the properties of individual QDs as well as array properties.

The Science Festival "Forskningens Døgn"
In April, we participated in the science festival "Forskninges Døgn" together with 6 other DNRF centres of excellence at DTU. It was a very good experience to tell about our research and passion for what we are doing.


Paper in Nature Photonics
Christian Anker Rosiek, Guillermo Arregui Bravo, and Søren Stobbe, together with collaborators at DTU - Technical University of Denmark, did the first experimental investigation of losses in photonic topological insulators, which have often been praised for their topological protection against backscattering. But the experiments, published in Nature Photonics, showed the opposite: Backscattering protection in integrated photonics is impossible with existing technologies, says study.
NanoPhoton turns three
On 1 April we celebrated that our centre turned three years. II t ahs been three fantastic years with much exciting research and very interesting results, and we look forward to the years to the years ahead of us.

Paper published in Physical Review Letters
Several NanoPhoton members and collaborators co-authored a paper in Physical Review Letters on "Cavity Optomechanics with Anderson-Localized Optical Modes”. The work demonstrates how the interaction of light and mechanical motion in suspended photonic nanostructures with narrow etched slots of several tenths of nanometers can be mediated by unavoidable fabrication imperfections and multiple scattering of light, the physics of which will matter as research in photonics approaches length scales on the order of the roughness.
Paper by Associate Professor Rasmus E Christiansen and co-authors in Optics Express
Associate Professor Rasmus E Christiansen and co-authors had their paper on "Impact of Figures of Merit in Photonic Inverse Design” published in Optics Express. Through inverse design, they demonstrate that markedly different photonic device geometries are needed to obtain optimal performance for applications with figures of merit of similar structure. Hereby stressing the importance of carefully analyzing, fully understanding and directly targeting the true device application in the inverse design process to obtain the best possible device performance.
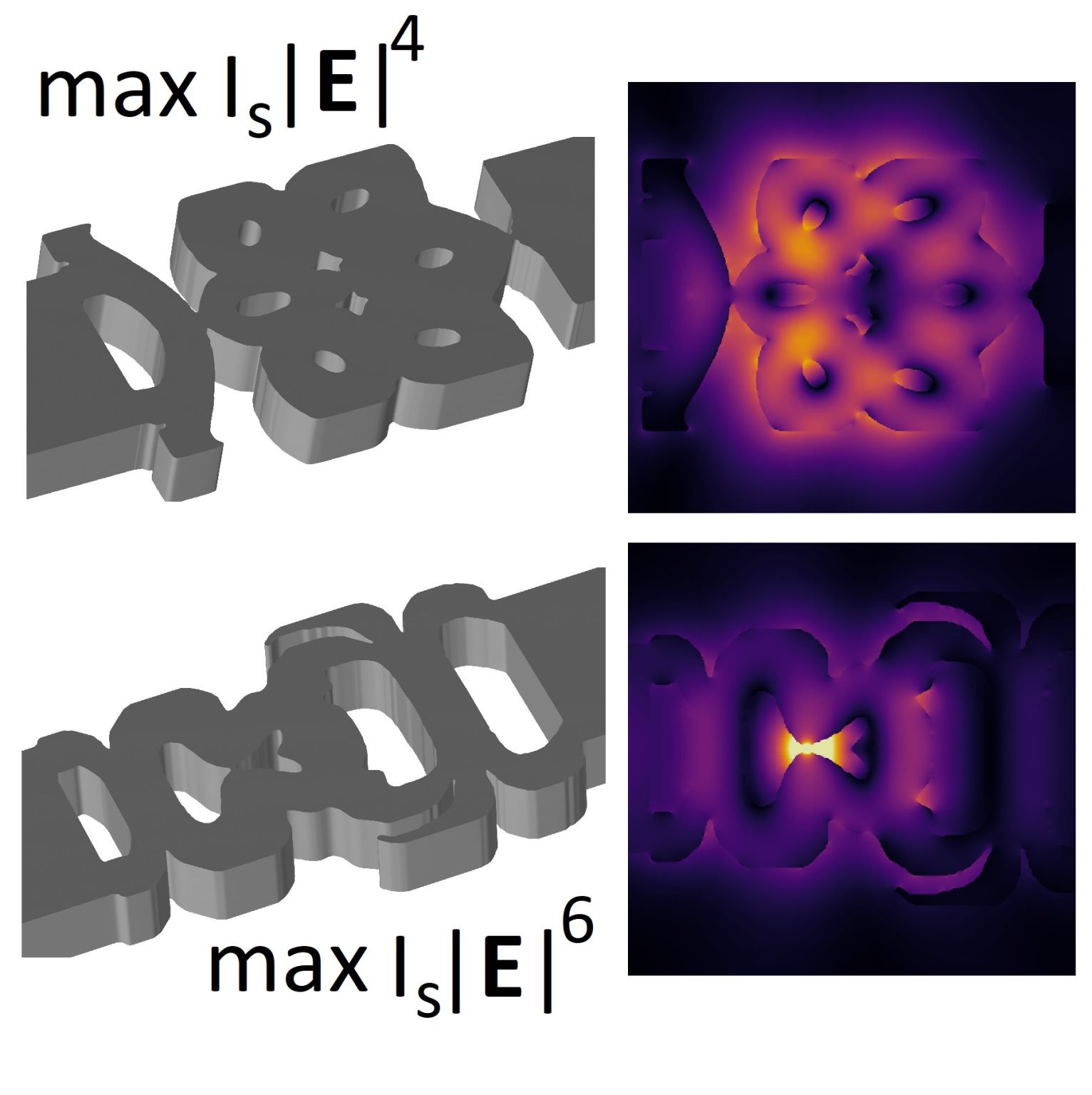
PhD defence by Laura Casses
On 24 February Laura Casses defended her PhD thesis on “Near-field exploration of light-matter interactions on gold and van der Waals materials”. Laura continues to work in the centre as a postdoc.

Paper in Optica on "Cavity dumping using a microscopic Fano laser"
Postdoc Gaoneng Dong had his paper on "Cavity dumping using a microscopic Fano laser" published in Optica. We demonstrate an ultra-small cavity-dumped microscopic laser based on an optical Fano resonance, which generates optical pulses with peak power more than one order of magnitude higher than the corresponding conventional gain-modulated laser. This demonstration paves the way for realizing microscopic lasers for low-power chip-scale applications. Link to the paper in the comment field.
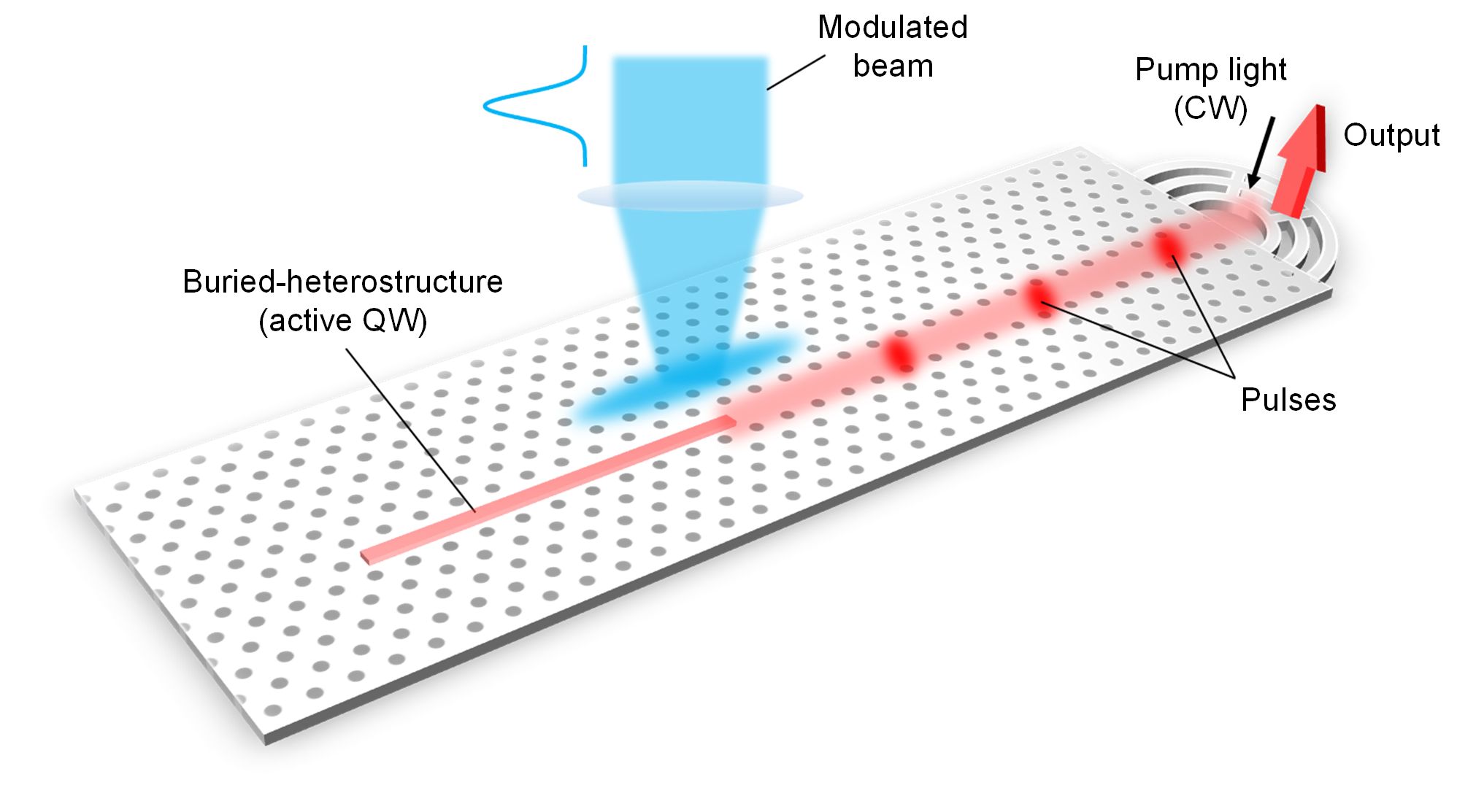
New members in NanoPhoton
Many new members have joined NanoPhoton in the past few months. They are Benjamin, Falkenberg Gøtzsche, PhD student, Pawel Holewa, postdoc, Mathias Marchal, PhD student, Adrian Holm Dubré, Research Assistant, and Simon Klinck Borregaard, PhD Student.





New member in NanoPhoton
In January we welcomed our newest member to NanoPhoton, senior researcher Thomas Christensen. Thomas is interested in the realization and manifestations of topological phenomena in photonic systems, especially in symmetry-protected topological phases. His expertise includes photonic crystal design and analysis, light-matter interaction, topological band theory, and group theory.

How to make LinkedIn work for us
In January we received a visit from Zydrune Domarkaite who gave a talk on “LinkedIn – how to make it work for you”. It was a very inspiring and motivating workshop. We hope the result will appear on our LinkedIN profile.

We are the cover story of the new edition of Laser Focus World
In the cover story of the new edition of Laser Focus World, PhD student Marcus Albrechtsen and Associate Professor Søren Stobbe share their thoughts on the perspectives of their recent results on dielectric bowtie cavities.
The new results were obtained in an interdisciplinary and highly collaborative team effort within NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics at DTU - Technical University of Denmark.

Søren Stobbe and his research group's scientific brealthorugh mentioned in the DNRF's newsletter
In their newsletter, The Danish National Research Foundation (DNRF) features an article with NanoPhoton member Søren Stobbe on his research group's recent scientific breakthrough. Congratulations to Søren and his group, and thanks to the DNRF.

New PhD student joining NanoPhoton
On 15 November we welcomed Amedeo Carbone to our centre. We look forward to working with you, Amedeo.

Workshop in NanoPhoton

We at NanoPhoton just held a workshop to get together, present our research, share ideas and strengthen collaboration across the centre. Thank you for the good talks and inspiration!
A feature article in Laser Focus World
The magazine Laser Focus World highlights our recent work on nanometer-scale photon confinement in topology-optimized dielectric cavities in a feature article!
Marco and Kristian participated in the “2022 IEEE Photonics Conference (IPC)” in Vancouver, Canada

Recently, our NanoPhoton members Marco Saldutti and Kristian Seegert took part in the “2022 IEEE Photonics Conference (IPC)” in Vancouver, Canada.
Kristian presented a microscopic laser – a so-called Fano laser – that uses a carefully engineered mirror to generate ultrashort pulses. The compact footprint makes this laser an attractive candidate as an on-chip pulsed light source for photonic integrated circuits.
Marco discussed the use of nonlinear photonic nanocavities with extreme dielectric confinement of light (EDC) for switching applications. The unconventional geometry enhances the diffusion dynamics of electron-hole pairs and allows a significant speed-up of all-optical signal processing functionalities, without compromising energy efficiency.
"Modal properties of dielectric bowtie cavities with deep sub-wavelength confinement"
In a recently published work in Optics Express, we at NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics performed a thorough numerical study of a novel semiconductor device that can squeeze light into the nanoscale with minimal losses, an important step in unlocking future quantum technologies.
Fundmental scientific breakthrough

Researchers from Søren Stobbe's research group have developed a nanostructure which compresses the light so that it becomes 10,000 times thinner than a human hair. This is a fundamental scientific breakthrough and can be important for multiple fields, including energy-efficient computers and quantum technology.
New colleagues joining us
On 1 September and 1 October, respectively, postdoc Alireza Shabani and PhD students Daniel Farbowitz and Sergei Lepeshov joined us at NanoPhoton.

New results with numerous applications published in "Nature Nanotechnology"
A new study led by researchers from the Catalan Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (ICN2, Barcelona) in collaboration with NanoPhoton researchers show that nanostructures can be engineered to either inhibit or guide mechanical vibrations at hypersonic frequencies. The results, published in the journal ‘Nature Nanotechnology’, could have numerous applications within nanotechnology, quantum computing, optomechanics, signal processing, and biosensors.
Please find the paper here:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-022-01178-1
NanoPhoton is growing
We are very glad to welcome our two new PhD students Beñat Martínez Aguirre de Jokisch and Robin Dahiya who joined NanoPhoton on 1 August.

"Electrically‐Driven Photonic Crystal Lasers with Ultra‐low Threshold" in Laser and Photonic Reviews
The latest issue of Laser and Photonic Reviews features our article titled "Electrically‐Driven Photonic Crystal Lasers with Ultra‐low Threshold" where we experimentally demonstrate a microscopic laser with ultra-low threshold developed at DTU and NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics. The properties of these lasers are investigated, providing new insight into the Quality Factor of the laser cavity, the leakage current, and efficiency.
Paper in Light: Science & Applications
Most theoretical derivations of fundamental radiative processes rely on energetic considerations and detailed balance equations, but not on momentum considerations. In this article we bring momentum exchange processes into consideration. It becomes very tricky in near-zero index (NZI) materials, i.e., materials having a phase refractive index close to zero. We theoretically demonstrate that momentum recoil, transfer momentum from the field to the atom and Doppler shift are inhibited in NZI materials. Fundamental radiative processes inhibition is also explained due to those momentum considerations inside three-dimensional NZI materials. We also discuss implication of NZI properties on consequence on the Heisenberg inequality, microscopy applications and diffraction pattern. Our findings give better understanding of fundamental light-matter interactions at the nanoscale as well as possibility of new lasing applications.
Momentum considerations inside near-zero index materials
Paper published in ACS Photonics
The team of Elizaveta Semenova demonstrated a novel InAs/InP Quantum Dot-based single photon emitter operating at the telecom C-band. A simple vertical emitting device possesses a photon extraction efficiency of ∼10% and high-purity single-photon generation ( g(2)(τ = 0) < 0.02 ) at the liquid helium temperature and preserved up to 50 K.
Bright Quantum Dot Single-Photon Emitters at Telecom Bands Heterogeneously Integrated on Si
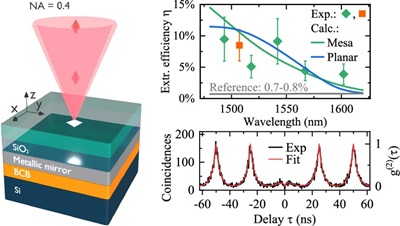
Conference on "Fundamentals and applications of semiconductor nanocavities"
Last week NanoPhoton hosted a conference on “Fundamentals and applications of semiconductor nanocavities” with 24 international leading researchers joining for three days of very good and interesting talks and vivid and fruitful discussions. Thank you to all for making it a success.

Three PhD Students join NanoPhoton



Kristian Seegert joined NanoPhoton on 1 March 2022. On 1 April 2022 Alexandra Palici and Frederik Schröder joined the centre. We look forward to the collaboration.
NanoPhoton Lecture: First-principles description of light-matter interactions in 2D materials by Kristian Sommer Thygesen
Kristian Thygesen develops and applies first-principles methods based on density functional theory and many-body perturbation theory to describe the electronic structure of materials with a particular focus on nanostructured and low-dimensional materials. He is also interested in the application of AI and data-driven approaches to materials design.
Two-dimensional (2D) materials, like graphene, hexagonal boron-nitride and the semiconducting transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), present exciting opportunities for creating new types of quantum states that can be manipulated with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. In this talk I will demonstrate how excitons in TMD monolayers may be tuned via dielectric engineering [1] and how (mixed) interlayer excitons in TMD bilayers [2] may be controlled by application of a perpendicular electrical field. The spontaneous radiative emission from electronic transitions in 2D materials can be manipulated by engineering the electromagnetic vacuum field. I will show that record high Purcell enhancements of up to 10^7 can be achieved by coupling intersubband transitions in van der Waals quantum wells to the acoustic plasmons in a graphene sheet [3]. Finally, I will discuss how first-principles calculations can aid the discovery of crystal point defects in wide band gap semiconductors with potential application as single-photon sources, spin qubits or magnetic field sensing [4].
Paper on "Quantum theory of two-dimensional materials coupled to electromagnetic resonators"
Recently published in Physical Review B, NanoPhoton research headed by Emil Denning shows how a series of recent spectacular experiments of strong coupling in systems of two-dimensional materials and nanoscale electromagnetic resonators can be explained by the symmetry-breaking light-matter interaction, which leads to the formation of a localized exciton state. In a companion letter in Physical Review Research, the team analyses the quantum optical properties of the strongly-coupled system, and predicts that polariton blockade due to nonlinear exciton-exciton interactions is well within reach by use of nanoscale resonators, such as the optical cavities designed and fabricated within the NanoPhoton research center.
Phys. Rev. B 105, 085306 (2022) - Quantum theory of two-dimensional materials coupled to electromagnetic resonators (aps.org)
Phys. Rev. Research 4, L012020 (2022) - Cavity-induced exciton localization and polariton blockade in two-dimensional semiconductors coupled to an electromagnetic resonator (aps.org)
NanoPhoton Lecture: III-V semiconductors on silicon hybrid nanophotonics by Fabrice Raineri
Raineri’s research activity is focused on the exploration of the interactions in III-V semiconductor/silicon hybrid photonic crystal (PhC) structures and their exploitation for the achievement of smaller, smarter, faster energy-efficient optoelectronic components which will revolutionize our world, governed by information and communication technology.
His aim is to build a new panel of optoelectronic devices, ultimate in terms of power consumption as well as in speed. His goal too is to trace new paths in nonlinear and quantum optics through the use of unprecedented optical configurations enabled by the hybrid approach. More in detail, he leads his work along three research directions namely, nanolasers, nonlinear nanophotonic devices and parametric nonlinear nanophotonics.
Proof of Concept Grant from the European Research Council (ERC) to demonstrate a new optical receiver for application in integrated photonics
The project, “Fano Detector”, is based on a novel idea of using a photonic Fano resonance to demodulate high-speed coherent signals in an energy-efficient way. The project builds on research results obtained in the ERC Advanced Grant “Fano Photonics”.
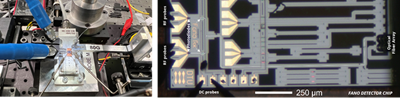
Measurement set-up (left) and chip (right) with coherent detector based on Fano interference.
Contacts:
Dr. Dagmawi Alemayehu Bekele
Prof. Jesper Mørk
ERC Press Release
@european-research-council
NanoPhoton paper published in NanoPhotonics
Elizaveta Semenova and Shima Kadkhodazadeh had their paper published in Nanophotonincs: Droplet epitaxy symmetric InAs/InP quantum dots for quantum emission in the third telecom window: morphology, optical and electronic properties.
We provide an analytical model to explain the kinetics of pit formation and QD base shape modification. Our theoretical calculations of electronic states reveal the properties of neutral and charged excitons and biexcitons confined in such QDs, which agree with the optical investigations of individual QDs. The optical response of QDs' ensemble suggests that FSS may indeed be negligible, as reflected in the vanishing degree of linear polarization.
NanoPhoton members to receive grants from the Velux Foundations

We are very proud to announce that two NanoPhoton members have received generous grants from the Velux Foundations. Senior Researcher Yi Yu receives DKK 6 million for his project ‘Nanolaser based on extremely confined nonradiative state (EXTREME)’. Thomas Christensen, who is currently a research scientist at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), receives DKK 8 million for his project 'Symmetry-guided discovery of topological photonics'.
PhD Student joins NanoPhoton
 |
We are very happy that Alisha Nanwani, PhD Student, joined NanoPhoton on 15 January 2022.
Alisha's project deals with selective epitaxy of III-V/Si nanostructures for extreme dielectric confinement of light.
|
Postdoc joins NanoPhoton
 |
We are very glad to welcome Yury Berdnikov, Postdoc, who joined NanoPhoton on 15 January 2022.
Yury's work is in between the nanofabrication in WP 4 and optoelectronic devices in WP 2. I investigate the ways for surface states passivation aiming to improve the optical performance of the structures with EDC cavities.
|
Postdoc joins NanoPhoton
 |
We are very pleased to announce that Mohammad Abutoama, postdoc, joined NanoPhoton on 15 December 2021.
Mohammad's research is focused on the interaction between colloidal Nanocrystal Quantum Dots (NQDs) and EDC cavities, including theoretical modeling, design and experimental realization of the light-matter interaction in NQDs-EDC nanostructures for proposing efficient single photon sources.
|
Yi Yu's paper published in Optica
Yi had his paper "Remote excitation between quantum emitters mediated by an optical Fano resonance" published in Optica.
We demonstrate remote coupling between two site-controlled semiconductor quantum dot emitters mediated by an optical Fano resonance induced by coupling cavity modes via a continuum waveguide state. Unlike ordinary coupled modes, the Fano mode offers both a spatially extended field and a high local density of optical states at the emitters, enhancing light–matter interaction.
NanoPhoton at MNE 2021 in Turin, Italy

NanoPhoton was represented at the "Micro and Nano Engineering Conference” (mne2021.org) in Turin, Italy by members Søren Stobbe, Ali Nawaz Babar, Marcus Albrechtsen and Søren Engelberth Hansen, seen here with DTU colleague Christian Anker Rosiek. The team presented recent work on Casimir forces in nanostructures, photonic topological insulators, and cavities with extreme dielectric confinement.
Paper on "Ultra-coherent Fano laser based on a bound state in the continuum" in Nature Photonics
In a recent paper in Nature Photonics, "Ultra-coherent Fano laser based on a bound state in the continuum", we show how a bound state in the continuum can be used to reduce the spectral linewidth of microlasers significantly. The microscopic laser developed at DTU Fotonik and NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics prove to have fundamental advantages compared to other lasers. Please, find the paper here.
NanoPhoton Lecture: Mesoscopic electrodynamics at metal surfaces: quantum and nonlocal effects by N. Asger Mortensen
Plasmonic phenomena in metals are commonly explored within the framework of classical electrodynamics and semiclassical models for the interactions of light with free-electron matter. The more detailed understanding of mesoscopic electrodynamics at metal surfaces is, however, becoming increasingly important for both fundamental developments in quantum plasmonics [1] and potential applications in emerging light-based quantum technologies [2]. While this intuitively calls for a full quantum description of plasmon-enhanced light-matter interactions, recent discoveries suggest how classical electrodynamics may still suffice if appropriately dressed by quantum-corrected mesoscopic boundary conditions – surface-response formalism. The colloquium will address three cases, where mesoscopic electrodynamic effects matter: 1) plasmon-emitter interactions [3], electronic surface states in crystalline materials [4], and plasmon-polariton interactions in graphene-on-metal structures [5]. Finally, prospects for probing electrodynamics of correlated electron materials are discussed [6].
References
[1] N.A. Mortensen, “Mesoscopic electrodynamics at metal surfaces – From quantum-corrected hydrodynamics to microscopic surface-response formalism”, Nanophotonics 10, 2563 (2021). [2] A.I. Fernández-Domínguez, S.I. Bozhevolnyi & N.A. Mortensen, “Plasmon-enhanced generation of non-classical light”, ACS Photonics 5, 3447 (2018). [3] P.A.D. Gonçalves et al., ”Plasmon-Emitter Interactions at the Nanoscale”, Nat. Commun. 11, 366 (2020). [4] A.R. Echarri et al., "Optical response of noble metal nanostructures: Quantum surface effects in crystallographic facets", Optica 8, 710 (2021). [5] P.A.D. Gonçalves et al., Quantum Surface-Response of Metals Revealed by Acoustic Graphene Plasmons", Nat. Commun. 12, 3271 (2021).
[6] A.T. Costa et al., "Harnessing Ultra-confined Graphene Plasmons to Probe the Electrodynamics of Superconductors", PNAS 118, e2012847118 (2021).
Tutorial papers in Top Downloads list for JOSA B
We are proud to see that our tutorial papers on inverse design in photonics by topology optimization jumped to the top of the Top Downloads list for JOSA B upon publication and remain on the list ten months later.
Utilize topology optimization to design an optical metalens, a demultiplexer or a plasmonic reflector, either by the click of a button in COMSOL Multiphysics https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.406048 or via a compact 200 line MATLAB code https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.405955.
Modal Properties of Photonic Crystal Cavities and Applications to Lasers
We have reviewed the properties of the resonant modes of photonic crystal cavities with a special focus on line-defect cavities and applications to ultra-small and energy-efficient semiconductor lasers including slow-light photonic crystal lasers and Fano lasers. We have also covered emerging cavities for extreme dielectric confinement, which promise extremely strong light–matter interactions with deep sub-wavelength mode size and a high quality factor.
You will find the paper here.
Official opening of NanoPhoton
We are very pleased to share some photos from the official opening ceremony of NanoPhoton - Center for Nanophotonics led by Prof. Jesper Mørk. It was a long-awaited and festive event. We extend our thanks to the Chairman of the Board of the Danmarks Grundforskningsfond/The Danish National Research Foundation, Prof. Jens Kehlet Nørskov, and the President of DTU, Prof. Anders Overgaard Bjarklev, for inspiring and supportive opening speeches. We also thank our collaborators and all of you who took the time to celebrate this wonderful occasion with us.

President of DTU, Prof. Anders Overgaard Bjarklev and
Center Leader of NanoPhoton, Prof. Jesper Mørk

Participants in the official opening of NanoPhoton

Jesper Mørk, Palle Jeppesen and Bjarne Tromborg

Members of NanoPhoton
Postdoc joins NanoPhoton
 |
We are pleased to announce that Ayman Nassar Kamel, Postdoc, joined NanoPhoton on 1 October.
Ayman works on the integration of EDC cavities with nano-electronic devices with a vision of providing a platform for sub-femto-joule-per-bit interconnects. He has experience in non-linear integrated optics and interface physics, both of which are useful for such nano-optoelectronic devices we hope to realize.
|
PhD Student joins NanoPhoton
 |
We are pleased to announce that Maria Vittoria Gurrieri,
PhD Student, joined NanoPhoton on 1 October.
Maria Vittoria works on the development of theoretical
models for light-matter interaction in EDC-structures.
Her research is focused on the investigation of such
interaction in optical nanocavities coupled with 2D
materials.
|
NanoPhoton Lecture: Single-photon quantum hardware: towards scalable photonic quantum technology with a quantum advantage by Peter Lodahl
Quantum dots embedded in photonic nanostructures offer a highly efficient and coherent deterministic photon-emitter interface [1]. It constitutes an on-demand single-photon source for quantum-information applications, enables single-photon nonlinear, optics and the constructing of deterministic quantum gates for photons [2]. We review recent experimental progress, and demonstrate that the current technology can be scaled up to reach quantum advantage [3] with the demonstration of near-transform-limited emitters in high-cooperativity planar nanophotonic waveguides [4]. The coherent control of a single spin in the quantum dot [5, 6] offers additional opportunities of generating advanced multi-photon entangled states [7]. We discuss potential applications of these novel deterministic photonic hardware in quantum computing and quantum communication [8], e.g., for constructing a resource efficient one-way quantum repeater [9].
References
[1] Lodahl et al., Rev. Mod. Phys. 87, 347 (2015). [2] Lodahl, Quantum Science and Technology 3, 013001 (2018). [3] Uppu et al., Science Advances 6, eabc8268 (2020). [4] Pedersen et al., ACS Photonics (2020). [5] Javadi et al., Nature Nanotechnology 13, 398 (2018). [6] Appel et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 013602 (2021). [7] Tiurev et al., Arxiv: 2007.09295. [8] Uppu et al., Arxiv: 2103.01110. [9] Borregaard et al., Phys. Rev. X 10, 021071 (2020).
NanoPhoton Lecture: From Photonic Crystals to Topological Nanophotonics by Masaya Notomi
NanoPhoton Lecture: Prospects and limitations of atomically thin semiconductors as laser gain material by Christopher Gies
NanoPhoton Lecture:Non-Radiating Electromagnetic Sources by Sergey I. Bozhevolnyi